Push buttons offer a simple momentary operation ideal for start/stop functions, while selector switches provide multiple stable positions for choosing different modes or settings. Discover how to choose the right control device for your application in the detailed comparison below.
Table of Comparison
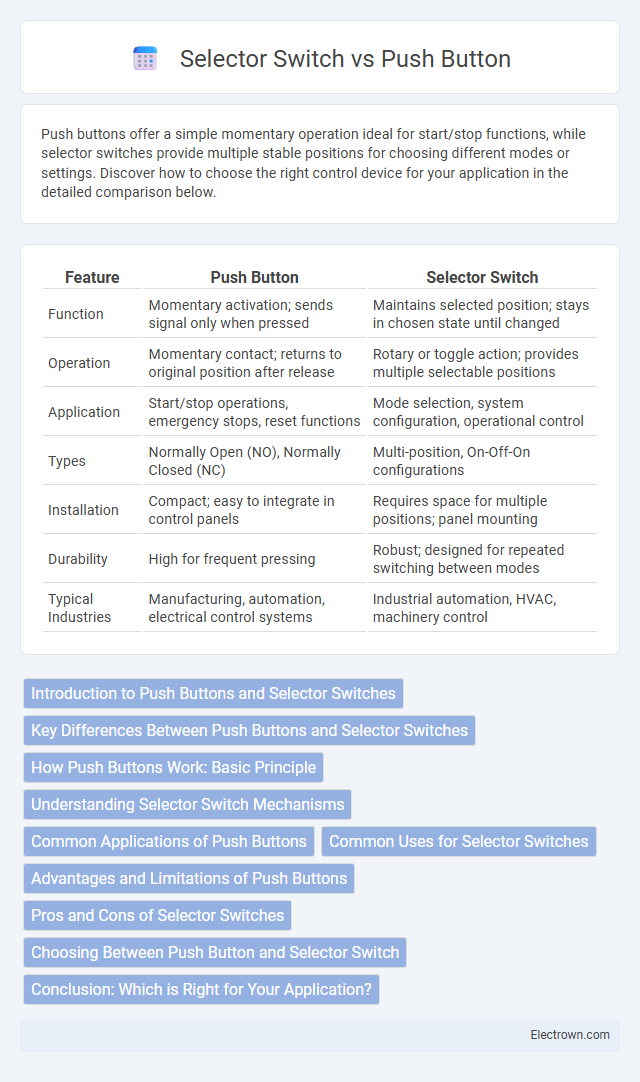
| Feature | Push Button | Selector Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Momentary activation; sends signal only when pressed | Maintains selected position; stays in chosen state until changed |
| Operation | Momentary contact; returns to original position after release | Rotary or toggle action; provides multiple selectable positions |
| Application | Start/stop operations, emergency stops, reset functions | Mode selection, system configuration, operational control |
| Types | Normally Open (NO), Normally Closed (NC) | Multi-position, On-Off-On configurations |
| Installation | Compact; easy to integrate in control panels | Requires space for multiple positions; panel mounting |
| Durability | High for frequent pressing | Robust; designed for repeated switching between modes |
| Typical Industries | Manufacturing, automation, electrical control systems | Industrial automation, HVAC, machinery control |
Introduction to Push Buttons and Selector Switches
Push buttons are simple control devices that enable momentary or maintained electrical circuit activation through a single press, commonly used in industrial machinery and control panels. Selector switches provide multiple-position selection for controlling circuit functions, allowing users to toggle between different modes or settings by rotating the switch to a desired position. Both push buttons and selector switches are critical components in control systems, offering reliable user interface options for operational commands and mode selection.
Key Differences Between Push Buttons and Selector Switches
Push buttons and selector switches differ primarily in their operation and application; push buttons provide momentary contact for immediate action, while selector switches maintain a selected position to control circuit states. Push buttons are ideal for start/stop functions, offering quick, temporary activation, whereas selector switches enable mode selection or system configuration with stable, lock-in positions. The mechanical design also varies: push buttons return to their original state after release, whereas selector switches stay locked until manually changed.
How Push Buttons Work: Basic Principle
Push buttons operate by completing or interrupting an electrical circuit when pressed, allowing current to flow momentarily to activate a connected device or function. They use a spring-loaded mechanism that returns the button to its original position once released, ensuring temporary operation. This simple on-off action distinguishes push buttons from selector switches, which maintain a selected position.
Understanding Selector Switch Mechanisms
Selector switches operate through a rotary mechanism that allows users to choose between multiple circuit options by turning the switch to a specific position. Unlike push buttons that complete or interrupt a circuit momentarily, selector switches maintain their position until manually changed, providing precise control over machinery or processes. Your understanding of selector switch mechanisms enhances the ability to implement reliable and user-friendly control panels in various industrial applications.
Common Applications of Push Buttons
Push buttons are commonly used in industrial machinery controls, elevator panels, and emergency stop systems due to their simple on/off functionality and easy activation. They provide momentary or maintained control signals essential for starting and stopping motors, triggering processes, or resetting alarms. Push buttons are favored in environments where quick, tactile feedback is necessary for operational safety and efficiency.
Common Uses for Selector Switches
Selector switches are commonly used in industrial control panels to enable users to choose between multiple operating modes or functions, such as starting, stopping, or switching between manual and automatic control. They provide clear visual feedback and tactile confirmation, enhancing safety and reducing operational errors in machinery and process control systems. Your control setup benefits from selector switches when precise mode selection and reliability are essential for efficient operation.
Advantages and Limitations of Push Buttons
Push buttons offer quick and intuitive control, making them ideal for emergency stops and frequent on/off operations due to their simple design and ease of use. They provide tactile feedback and can be easily integrated into compact control panels, but their momentary contact nature limits their function to temporary activation unless combined with latching mechanisms. Push buttons may also be less suitable for applications requiring multiple distinct operational states, where selector switches provide clearer positional control.
Pros and Cons of Selector Switches
Selector switches offer clear, intuitive operation with multiple position options, making them ideal for complex control systems. They provide reliable, tactile feedback and are less prone to accidental activation, enhancing safety and precision. However, selector switches can be bulkier and more expensive than push buttons, and their fixed positions may limit flexibility in dynamic control scenarios.
Choosing Between Push Button and Selector Switch
Choosing between a push button and a selector switch depends on the application's operational requirements and user interface design. Push buttons are ideal for momentary actions or single commands, offering quick response and ease of use, while selector switches provide multiple fixed positions for mode selection or operational states, enhancing control versatility. Consider factors like frequency of use, required feedback, and safety standards to determine the optimal switch type for industrial or consumer devices.
Conclusion: Which is Right for Your Application?
Push buttons provide quick, momentary control ideal for start-stop commands, while selector switches offer stable, maintained positions suited for mode or function selection. Your choice depends on operational needs: push buttons excel in dynamic, immediate actions; selector switches are preferred for toggle functionality and clear status indication. Evaluating the specific control requirements and user interaction ensures selecting the right switch for your application.
Push Button vs Selector Switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com