Transient voltage suppressors provide rapid, precise protection against voltage spikes by clamping excess voltage to safe levels, while surge protectors offer broader defense by diverting large surges away from connected devices through components like metal oxide varistors. Understanding the differences helps you choose the best solution for safeguarding your electronics; explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
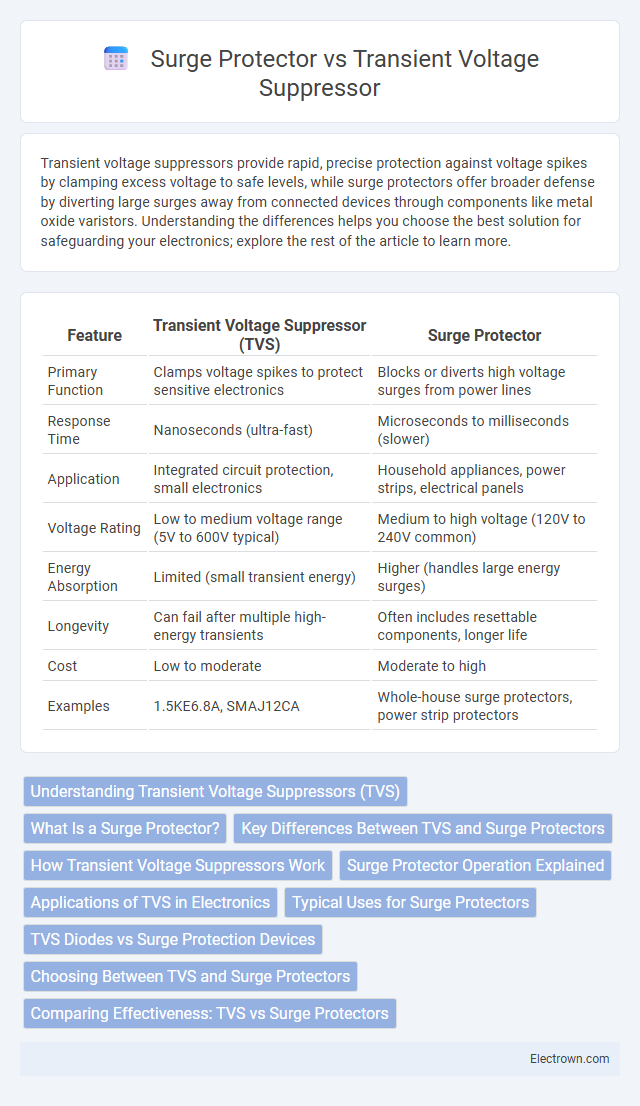
| Feature | Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) | Surge Protector |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Clamps voltage spikes to protect sensitive electronics | Blocks or diverts high voltage surges from power lines |
| Response Time | Nanoseconds (ultra-fast) | Microseconds to milliseconds (slower) |
| Application | Integrated circuit protection, small electronics | Household appliances, power strips, electrical panels |
| Voltage Rating | Low to medium voltage range (5V to 600V typical) | Medium to high voltage (120V to 240V common) |
| Energy Absorption | Limited (small transient energy) | Higher (handles large energy surges) |
| Longevity | Can fail after multiple high-energy transients | Often includes resettable components, longer life |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Examples | 1.5KE6.8A, SMAJ12CA | Whole-house surge protectors, power strip protectors |
Understanding Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS)
Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) are semiconductor devices designed to protect electronic circuits from sudden voltage spikes by clamping excessive voltages to safe levels within nanoseconds. Unlike surge protectors that typically use metal oxide varistors (MOVs) and are intended for broader protection against power surges, TVS diodes offer rapid response and precise voltage regulation, essential for sensitive electronics and communication lines. Your equipment benefits from TVS technology through enhanced defense against transient overvoltages caused by lightning, switching actions, or electrostatic discharge.
What Is a Surge Protector?
A surge protector is a device designed to shield electrical appliances from voltage spikes by diverting excess electricity to the ground. It typically uses metal oxide varistors (MOVs) to absorb and dissipate transient surges caused by lightning, power outages, or switching activities. Surge protectors safeguard sensitive electronics by maintaining voltage within safe limits, preventing damage and extending device lifespan.
Key Differences Between TVS and Surge Protectors
Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) are designed to react instantly to transient voltage spikes, clamping high-voltage surges to protect sensitive electronic components from damage. Surge protectors, often used in household and industrial settings, provide broader protection by diverting excess voltage from electrical devices during power surges, including lightning strikes and switching events. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right device to safeguard your equipment based on response time, application scale, and surge energy capacity.
How Transient Voltage Suppressors Work
Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) protect electronic circuits by clamping voltage spikes and absorbing transient surges, preventing damage caused by sudden power surges or electrostatic discharges. They operate by rapidly switching to a low-resistance state when voltage exceeds a specific threshold, diverting excess current away from sensitive components. This fast response time makes TVS devices essential for safeguarding semiconductor devices and communication lines against transient overvoltages.
Surge Protector Operation Explained
Surge protectors operate by diverting excess voltage from transient spikes away from connected devices, using components like Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) that clamp voltage to safe levels. This rapid response prevents damage caused by sudden surges, typically originating from lightning strikes or power fluctuations. Unlike basic power strips, surge protectors provide a critical defense by absorbing and dissipating dangerous transient voltages.
Applications of TVS in Electronics
Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) are widely applied in electronics to protect sensitive components from voltage spikes caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, and inductive load switching. TVS devices are crucial in automotive electronics, telecommunications, and industrial control systems where rapid transient suppression ensures device reliability and longevity. Your electronic systems benefit from TVS by maintaining stable operation and preventing damage in environments prone to transient voltage events.
Typical Uses for Surge Protectors
Surge protectors are commonly used to safeguard household electronics such as computers, televisions, and gaming consoles from power surges caused by lightning strikes or switching operations. They are ideal for protecting sensitive devices connected to standard power outlets in residential and office environments. Your valuable electronics benefit from surge protectors by preventing damage and prolonging their lifespan during unexpected voltage spikes.
TVS Diodes vs Surge Protection Devices
TVS diodes provide rapid clamping of transient voltage spikes by responding within picoseconds, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from ESD and fast transients. Surge protection devices (SPDs), such as metal oxide varistors (MOVs), absorb and dissipate larger energy surges like lightning strikes or power surges over longer durations, offering bulk power protection. TVS diodes excel in precision and speed, while SPDs handle high-energy surges, making their combined use essential for comprehensive electrical surge protection systems.
Choosing Between TVS and Surge Protectors
Choosing between transient voltage suppressors (TVS) and surge protectors depends on the specific application and voltage spike characteristics. TVS devices offer rapid response times and precise clamping for transient voltage spikes in sensitive electronics, often used in circuit boards and communication lines. Surge protectors provide broader protection against high-energy surges, such as lightning strikes or power surges, making them suitable for household appliances and industrial equipment.
Comparing Effectiveness: TVS vs Surge Protectors
Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) provide rapid response to voltage spikes by clamping transient voltages within nanoseconds, making them highly effective for protecting sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge and switching transients. Surge protectors, typically incorporating metal oxide varistors (MOVs), offer broader protection by absorbing larger energy surges from lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations but react more slowly compared to TVS diodes. The effectiveness of TVS devices excels in low-energy, high-speed transient scenarios, while surge protectors are more suitable for high-energy, longer-duration surges, making their combined use ideal for comprehensive surge mitigation.
Transient Voltage Suppressor vs Surge Protector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com