Dielectric sensors measure changes in a material's dielectric constant to detect object presence or composition, while capacitive sensors detect proximity or changes in capacitance caused by nearby conductive or dielectric objects. Discover how understanding these differences can enhance Your sensor selection in various applications by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
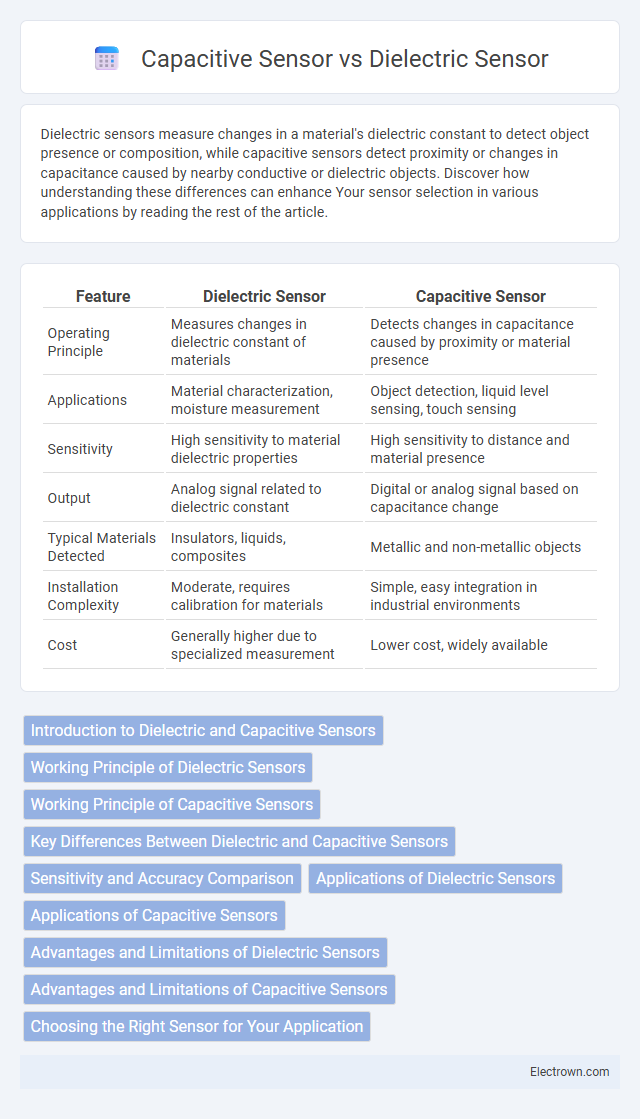
| Feature | Dielectric Sensor | Capacitive Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Measures changes in dielectric constant of materials | Detects changes in capacitance caused by proximity or material presence |
| Applications | Material characterization, moisture measurement | Object detection, liquid level sensing, touch sensing |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to material dielectric properties | High sensitivity to distance and material presence |
| Output | Analog signal related to dielectric constant | Digital or analog signal based on capacitance change |
| Typical Materials Detected | Insulators, liquids, composites | Metallic and non-metallic objects |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate, requires calibration for materials | Simple, easy integration in industrial environments |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized measurement | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Dielectric and Capacitive Sensors
Dielectric sensors measure changes in material properties by detecting variations in permittivity, offering precise detection of solids and liquids. Capacitive sensors operate by sensing changes in capacitance caused by the proximity or presence of conductive or dielectric materials, widely used for non-contact object detection. Your choice between these sensors depends on the specific application requirements, such as sensitivity to material type and environmental conditions.
Working Principle of Dielectric Sensors
Dielectric sensors operate by measuring changes in the dielectric constant of a material, which directly affects the sensor's capacitance value as the material interacts with the electric field. These sensors detect variations in permittivity caused by the presence or absence of different substances, enabling precise detection of moisture, humidity, or material composition. Unlike simple capacitive sensors, dielectric sensors are finely tuned to detect subtle changes in dielectric properties, providing enhanced sensitivity for applications in industrial and environmental monitoring.
Working Principle of Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive sensors operate by detecting changes in the dielectric constant of the material between two conductive plates, which influences the capacitance value. When an object comes close or touches the sensor, it alters the electric field, causing measurable variations in capacitance. Your applications benefit from capacitive sensors' sensitivity to non-metallic materials, liquids, and proximity detection without physical contact.
Key Differences Between Dielectric and Capacitive Sensors
Dielectric sensors measure changes in the dielectric constant of a material, offering precise detection of different substances based on their electrical properties. Capacitive sensors detect changes in capacitance caused by the proximity or presence of conductive or dielectric objects, commonly used for touch and position sensing. Understanding the key differences helps you select the right sensor for applications requiring material identification versus proximity detection.
Sensitivity and Accuracy Comparison
Dielectric sensors exhibit higher sensitivity to changes in material properties, making them ideal for detecting subtle variations in dielectric constants, while capacitive sensors provide accurate measurements primarily influenced by changes in geometry and distance between plates. Capacitive sensors excel in precision for position and proximity detection due to stable capacitance responses, whereas dielectric sensors offer superior accuracy in applications involving complex material characterization. Sensitivity in dielectric sensors is often enhanced by frequency modulation, whereas capacitive sensors rely on high-resolution circuitry to maximize accuracy.
Applications of Dielectric Sensors
Dielectric sensors excel in applications requiring precise measurement of material properties such as moisture content, thickness, and composition in industries like agriculture, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. Their ability to detect changes in dielectric constant enables non-destructive testing and quality control in polymers, ceramics, and composite materials. These sensors are also critical in monitoring soil moisture for irrigation management and in fuel level sensing within automotive and aerospace sectors.
Applications of Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive sensors are widely used in touchscreen devices, proximity sensing, and level measurement in liquids and powders. They excel in detecting conductive and non-conductive materials without physical contact, making them ideal for industrial automation, consumer electronics, and automotive safety systems. Their sensitivity and reliability enable precise measurement in humid or dusty environments where dielectric sensors may face challenges.
Advantages and Limitations of Dielectric Sensors
Dielectric sensors offer advantages such as high sensitivity to variations in material properties, enabling precise detection of moisture content and chemical composition. Their limitations include susceptibility to temperature fluctuations and lower accuracy in heterogeneous materials compared to capacitive sensors. Despite these challenges, dielectric sensors provide valuable real-time analysis in applications like soil monitoring and industrial quality control.
Advantages and Limitations of Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive sensors offer high sensitivity and can detect a wide range of materials, including liquids and solids, making them ideal for diverse industrial applications. Their non-contact measurement reduces wear and extends sensor life, but they can be affected by environmental factors like humidity and temperature variations, which may cause signal drift. You should consider these limitations when precision and environmental conditions are critical for sensor performance.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Dielectric sensors measure changes in a material's dielectric constant, making them ideal for detecting non-metallic substances and moisture content with high accuracy. Capacitive sensors, relying on variations in capacitance between sensor plates, excel in proximity sensing and detecting metallic or conductive objects in industrial automation. Selecting the right sensor depends on the target material properties and environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in applications ranging from liquid level detection to object presence sensing.
dielectric sensor vs capacitive sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com