DMMs (Digital Multimeters) offer versatile measurements including voltage, current, and resistance, while LCR meters specialize in accurately measuring inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) for electronic components. Discover how choosing the right instrument can enhance your testing precision and efficiency by exploring the rest of the article.
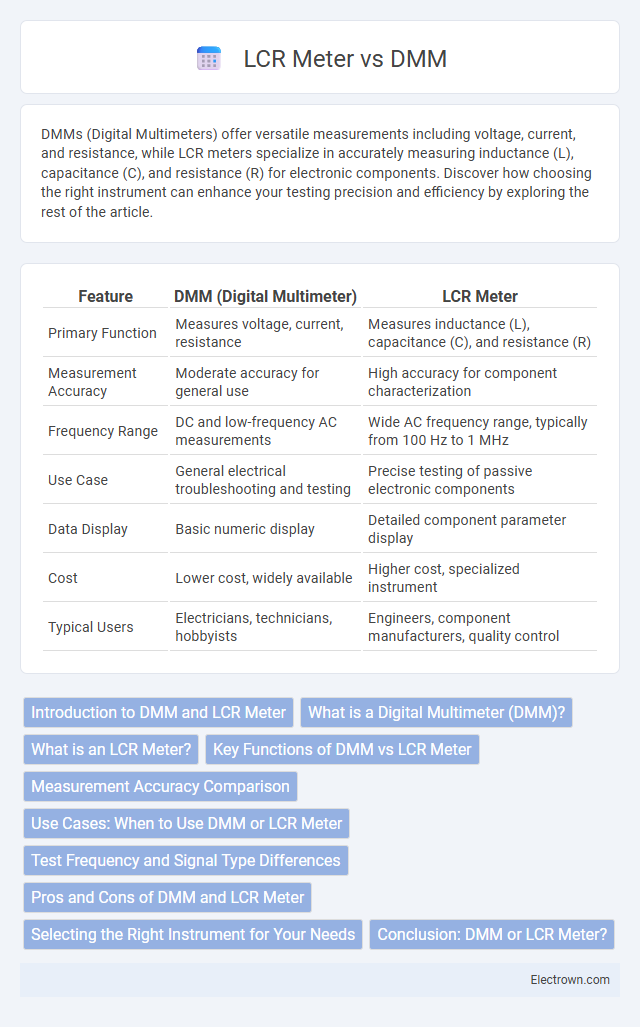
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DMM (Digital Multimeter) | LCR Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures voltage, current, resistance | Measures inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) |
| Measurement Accuracy | Moderate accuracy for general use | High accuracy for component characterization |
| Frequency Range | DC and low-frequency AC measurements | Wide AC frequency range, typically from 100 Hz to 1 MHz |
| Use Case | General electrical troubleshooting and testing | Precise testing of passive electronic components |
| Data Display | Basic numeric display | Detailed component parameter display |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized instrument |
| Typical Users | Electricians, technicians, hobbyists | Engineers, component manufacturers, quality control |
Introduction to DMM and LCR Meter
A Digital Multimeter (DMM) is an essential handheld instrument used to measure voltage, current, and resistance with digital precision, widely favored for troubleshooting electrical circuits. An LCR meter specializes in measuring inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) of electronic components, providing detailed insight into component characteristics for circuit design and testing. Both instruments serve critical roles in electronics, with the DMM offering broad electrical measurement capabilities and the LCR meter delivering focused component analysis.
What is a Digital Multimeter (DMM)?
A Digital Multimeter (DMM) is a versatile electronic measuring instrument used to measure voltage, current, resistance, and sometimes other electrical parameters such as capacitance and frequency. It provides digital readouts for accurate and easy-to-read measurements, making it essential for troubleshooting and testing electrical circuits and components. Your ability to quickly diagnose electrical issues improves significantly when using a DMM compared to specialized meters like LCR meters.
What is an LCR Meter?
An LCR meter measures inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) in electronic components, providing precise data for circuit analysis and troubleshooting. Unlike a digital multimeter (DMM), which primarily measures voltage, current, and resistance, an LCR meter specializes in assessing component values critical for frequency-dependent applications. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed component characterization (LCR meter) or general electrical measurements (DMM).
Key Functions of DMM vs LCR Meter
A Digital Multimeter (DMM) primarily measures voltage, current, and resistance with high accuracy, making it essential for general electrical troubleshooting and diagnostics. An LCR meter specializes in measuring inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R), providing detailed analysis of passive electronic components' properties. Your choice depends on whether you need broad electrical testing (DMM) or precise component characterization (LCR meter).
Measurement Accuracy Comparison
DMMs (Digital Multimeters) typically provide measurement accuracy ranging from 0.05% to 0.5% for voltage and resistance, suitable for general electronic testing. LCR meters specialize in measuring inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) with higher precision, often achieving accuracy better than 0.1%, making them ideal for component characterization. Choosing between a DMM and an LCR meter depends on your need for precision in complex impedance measurements versus versatile electrical quantity testing.
Use Cases: When to Use DMM or LCR Meter
DMMs are ideal for general-purpose electrical testing, measuring voltage, current, and resistance in circuits, making them essential for troubleshooting and diagnostics in electronics and electrical maintenance. LCR meters specialize in precise measurement of inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) of components, critical for component characterization, quality control, and circuit design in RF and passive component testing. Use a DMM for routine electrical tasks and an LCR meter for detailed component analysis where accuracy in reactive parameters is required.
Test Frequency and Signal Type Differences
DMMs (Digital Multimeters) typically use low-frequency DC or low AC test signals, which are suitable for measuring voltage, current, and resistance but provide limited accuracy at high frequencies. LCR meters employ higher-frequency AC test signals, ranging from a few hundred hertz up to several megahertz, enabling precise measurement of inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) parameters. The choice of test frequency and signal type directly impacts measurement accuracy and component characterization, with LCR meters optimized for frequency-dependent impedance analysis.
Pros and Cons of DMM and LCR Meter
DMMs (Digital Multimeters) offer versatile measurements including voltage, current, and resistance, making them great for general electrical testing but often lack the precision for inductance and capacitance readings. LCR meters specialize in measuring inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) with high accuracy, ideal for component testing but are typically more expensive and less versatile than DMMs. Choosing between a DMM and an LCR meter depends on the specific measurement needs, with DMMs favored for broad electrical diagnostics and LCR meters preferred for detailed component characterization.
Selecting the Right Instrument for Your Needs
Choosing between a Digital Multimeter (DMM) and an LCR meter depends on the specific measurements you require; a DMM offers versatility for voltage, current, and resistance, while an LCR meter specializes in precise inductance, capacitance, and resistance testing. Your selection should prioritize the instrument's accuracy, frequency range, and ease of use to match your testing environment and component types. Understanding these key differences helps ensure you invest in a tool that optimally supports your electronics diagnostics and troubleshooting tasks.
Conclusion: DMM or LCR Meter?
Choosing between a Digital Multimeter (DMM) and an LCR meter depends on the specific measurement needs; a DMM is ideal for basic voltage, current, and resistance testing, while an LCR meter specializes in precise inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) measurements. Your decision should prioritize accuracy and functionality relevant to your electronic testing tasks. For detailed component characterization, an LCR meter offers superior performance, whereas a DMM provides versatile, general-purpose diagnostics.
DMM vs LCR meter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com