SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) operates in sync with the system clock, offering improved performance over traditional DRAM, while DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM) enhances this technology by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, effectively doubling the data transfer rate. Discover how these differences impact your computer's speed and efficiency by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
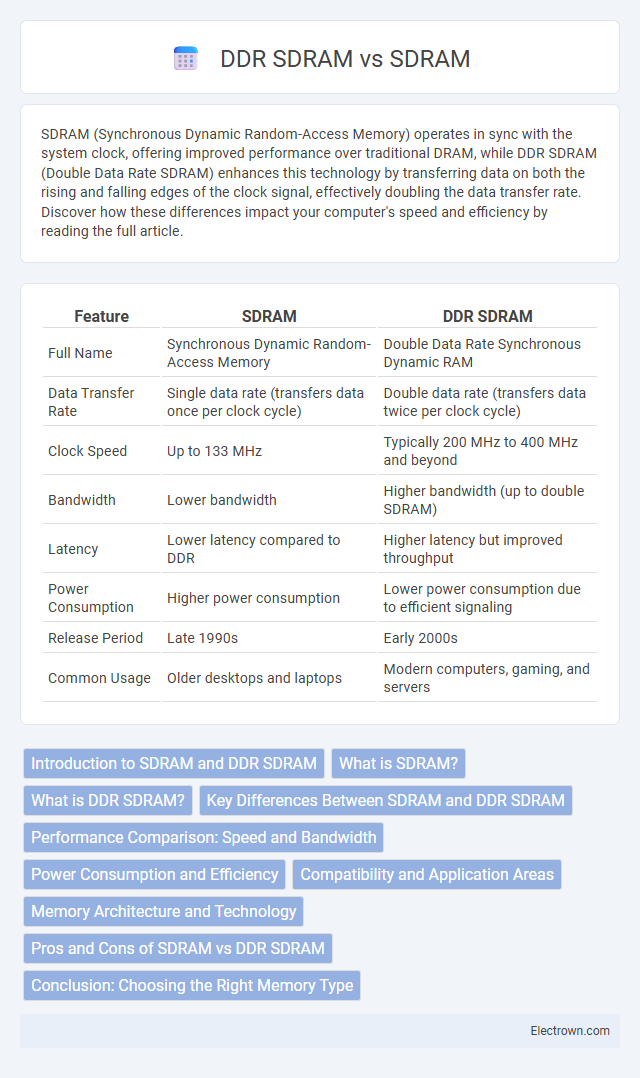
| Feature | SDRAM | DDR SDRAM |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory | Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic RAM |
| Data Transfer Rate | Single data rate (transfers data once per clock cycle) | Double data rate (transfers data twice per clock cycle) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 133 MHz | Typically 200 MHz to 400 MHz and beyond |
| Bandwidth | Lower bandwidth | Higher bandwidth (up to double SDRAM) |
| Latency | Lower latency compared to DDR | Higher latency but improved throughput |
| Power Consumption | Higher power consumption | Lower power consumption due to efficient signaling |
| Release Period | Late 1990s | Early 2000s |
| Common Usage | Older desktops and laptops | Modern computers, gaming, and servers |
Introduction to SDRAM and DDR SDRAM
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) synchronizes with the system clock to improve performance over older asynchronous memory types. DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM) enhances this by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, effectively doubling the data rate. Your computer's memory speed and responsiveness heavily depend on these technologies, with DDR SDRAM providing faster, more efficient data processing than traditional SDRAM.
What is SDRAM?
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) is a type of memory that synchronizes with the system clock to improve the timing and speed of data access compared to conventional DRAM. DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM) builds on SDRAM technology by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, effectively doubling the data rate. Understanding the distinction between SDRAM and DDR SDRAM helps you optimize your computer's memory performance and compatibility.
What is DDR SDRAM?
DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) is an advanced type of SDRAM that transfers data twice per clock cycle, effectively doubling the data throughput compared to traditional SDRAM. This technology enhances Your system's memory performance by enabling faster data access and improved bandwidth, making it ideal for modern computing applications. DDR SDRAM's ability to operate at higher frequencies while maintaining synchronization with the system clock provides significant speed advantages over standard SDRAM.
Key Differences Between SDRAM and DDR SDRAM
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) operates with a single data rate, transferring data once per clock cycle, while DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM) transfers data twice per clock cycle, effectively doubling the data transfer rate. DDR SDRAM offers improved performance and higher bandwidth compared to standard SDRAM, making it more suitable for modern computing needs. Your system benefits from DDR SDRAM with faster memory access and better overall efficiency in handling multitasking and complex applications.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Bandwidth
DDR SDRAM offers significant performance improvements over traditional SDRAM by doubling data transfer rates through its double data rate architecture, effectively increasing speed and bandwidth. Your system benefits from DDR SDRAM's ability to transfer data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, resulting in higher throughput and more efficient memory utilization. As a result, DDR SDRAM is the preferred choice for applications requiring faster data access and greater bandwidth capabilities compared to standard SDRAM.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
DDR SDRAM significantly improves power consumption and efficiency compared to traditional SDRAM by operating at lower voltages, typically 1.8V or 1.5V versus SDRAM's standard 3.3V. This reduction not only minimizes energy usage but also enhances overall system performance through faster data transfer rates and better signal integrity. As a result, DDR SDRAM is preferred in modern computing applications where energy efficiency and higher throughput are critical.
Compatibility and Application Areas
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) and DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM) differ significantly in compatibility, as DDR SDRAM is not backward compatible with older SDRAM slots due to differing pin configurations and signaling protocols. DDR SDRAM is predominantly used in modern desktops, laptops, and gaming consoles for faster data transfer rates and improved performance, while SDRAM remains limited to legacy systems and older hardware configurations. Compatibility constraints require careful selection based on motherboard support and intended application areas, with DDR SDRAM favored for memory-intensive tasks and multitasking environments.
Memory Architecture and Technology
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) uses a single data rate architecture that synchronizes with the system clock to improve data transfer efficiency, while DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM) enhances this by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock cycle, effectively doubling the data rate without increasing the clock frequency. DDR SDRAM incorporates advanced prefetch architecture, typically fetching 2 bits per clock cycle compared to SDRAM's 1-bit prefetch, which significantly boosts bandwidth and performance. Understanding these differences in memory architecture and technology helps you select the right memory type for faster and more efficient computing.
Pros and Cons of SDRAM vs DDR SDRAM
SDRAM offers stable performance and synchronization with the processor clock, making it reliable for basic computing tasks, but its throughput is limited compared to DDR SDRAM. DDR SDRAM doubles data transfer rates by transferring data on both clock edges, resulting in higher bandwidth and improved multitasking capabilities, yet it consumes slightly more power and can be costlier. Consider your system requirements and budget to determine if the enhanced speed of DDR SDRAM aligns with your performance needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Memory Type
SDRAM offers basic synchronous memory performance suitable for older systems, while DDR SDRAM provides faster data transfer rates by doubling the memory clock frequency, making it ideal for modern computing demands. Selecting DDR SDRAM enhances system speed and efficiency due to its improved bandwidth and lower latency compared to traditional SDRAM. Compatibility with the motherboard and intended application should guide the choice between these memory types to ensure optimal performance.
SDRAM vs DDR SDRAM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com