Poly resistors offer stable resistance and are commonly used in integrated circuits due to their precision and temperature stability, while diffusion resistors provide simpler fabrication but can suffer from variability and less precision. To understand which resistor type best suits your electronic design needs, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
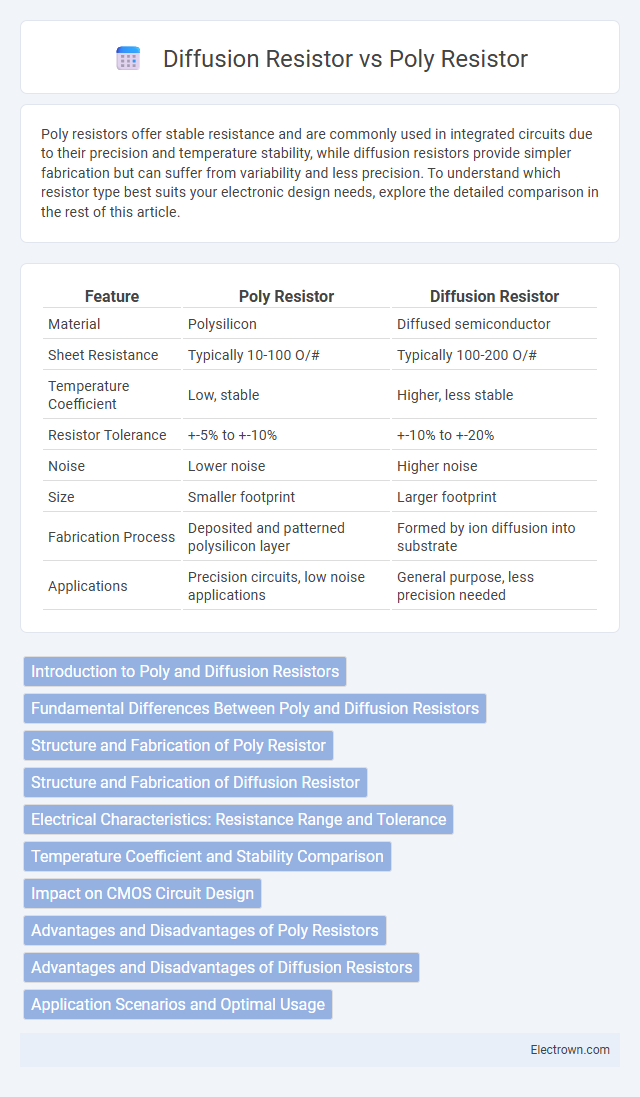
| Feature | Poly Resistor | Diffusion Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polysilicon | Diffused semiconductor |
| Sheet Resistance | Typically 10-100 O/# | Typically 100-200 O/# |
| Temperature Coefficient | Low, stable | Higher, less stable |
| Resistor Tolerance | +-5% to +-10% | +-10% to +-20% |
| Noise | Lower noise | Higher noise |
| Size | Smaller footprint | Larger footprint |
| Fabrication Process | Deposited and patterned polysilicon layer | Formed by ion diffusion into substrate |
| Applications | Precision circuits, low noise applications | General purpose, less precision needed |
Introduction to Poly and Diffusion Resistors
Poly resistors are semiconductor components made by depositing polycrystalline silicon on a substrate, offering precise control over resistance and excellent thermal stability. Diffusion resistors are formed by diffusing impurities into the silicon substrate, resulting in a resistor with distinct electrical characteristics and moderate temperature coefficients. Your choice between poly and diffusion resistors depends on the required resistance accuracy, thermal performance, and integration compatibility within semiconductor devices.
Fundamental Differences Between Poly and Diffusion Resistors
Poly resistors, built using polysilicon layers, offer higher sheet resistance and better temperature stability compared to diffusion resistors, which are formed by doping the substrate. Diffusion resistors exhibit lower sheet resistance and are more prone to process variations affecting their resistance value. The fundamental differences lie in their fabrication methods, electrical characteristics, and temperature coefficients, influencing their selection in integrated circuit designs.
Structure and Fabrication of Poly Resistor
Poly resistors are typically fabricated using a thin film of doped polysilicon deposited on a silicon substrate, formed through photolithography and etching processes to define precise resistor geometries. The polysilicon layer's microstructure, influenced by doping concentration and annealing, provides a stable resistance ideal for integrated circuits. Understanding the poly resistor's fabrication enables you to optimize performance and integration in semiconductor device design.
Structure and Fabrication of Diffusion Resistor
Diffusion resistors are formed by doping a semiconductor substrate through ion diffusion, creating a highly controlled resistive region with specific electrical properties. This process involves introducing impurities into the silicon wafer, allowing precise adjustment of resistance by varying dopant concentration and diffusion depth. In contrast, poly resistors are fabricated using polycrystalline silicon layers deposited and patterned on the wafer, enabling different electrical characteristics and integration methods.
Electrical Characteristics: Resistance Range and Tolerance
Poly resistors typically offer a wide resistance range from a few ohms to several megaohms with tolerances around +-5% to +-10%, making them suitable for general-purpose applications requiring moderate precision. Diffusion resistors provide narrower resistance ranges, often limited to kilo-ohms, but boast tighter tolerance levels of +-1% or better, enhancing accuracy in precision circuits. Your choice depends on whether a broader resistance spectrum or higher precision tolerance is critical for your electrical design.
Temperature Coefficient and Stability Comparison
Poly resistors typically exhibit a lower temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) around +-100 ppm/degC, providing better stability over temperature variations compared to diffusion resistors, which can have TCR values exceeding +-300 ppm/degC. The lower TCR in poly resistors results from their stable polysilicon material structure, enhancing performance in precision analog circuits where temperature-induced resistance shifts must be minimized. Diffusion resistors, formed by doping silicon substrate, tend to be less stable due to higher sensitivity to temperature changes and process variations, making poly resistors more favorable for applications requiring tight tolerance and long-term stability.
Impact on CMOS Circuit Design
Poly resistors and diffusion resistors differ significantly in their impact on CMOS circuit design due to variations in sheet resistance and noise characteristics. Poly resistors offer higher sheet resistance and better temperature stability, making them ideal for precision analog circuits and biasing applications in CMOS designs. Your choice between the two affects circuit performance, power consumption, and noise margins, influencing overall device reliability and efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Poly Resistors
Poly resistors offer advantages such as higher precision, better temperature stability, and increased reliability compared to diffusion resistors, making them ideal for integrated circuits requiring consistent performance. Their manufacturing process allows for tighter tolerance control and lower noise levels, but poly resistors typically have higher resistance values and can be more expensive to produce. Your design choice depends on whether precision and stability outweigh cost and resistance range in your application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Diffusion Resistors
Diffusion resistors offer precise resistance values and excellent thermal stability due to their construction within the semiconductor substrate, making them ideal for integrated circuits requiring high accuracy. However, they typically exhibit higher noise levels and larger variations in resistance compared to poly resistors, which can impact performance in sensitive analog applications. The fabrication process of diffusion resistors also tends to be less flexible, limiting customization and scalability compared to polysilicon resistors.
Application Scenarios and Optimal Usage
Poly resistors are ideal for integrated circuits requiring high stability and precise resistance values, commonly used in analog signal processing and RF applications due to their excellent temperature coefficient and noise performance. Diffusion resistors suit applications demanding high resistance values within compact areas, often found in digital circuits and MOSFET biasing where linearity and process compatibility are critical. Your choice between poly and diffusion resistors depends on the specific circuit requirements for precision, thermal stability, and area efficiency.
Poly Resistor vs Diffusion Resistor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com