Direct Mount and Flip Chip are advanced semiconductor packaging techniques that enhance chip performance by minimizing signal path lengths and improving thermal management. Explore the article to understand how each method impacts your device's efficiency and reliability.
Table of Comparison
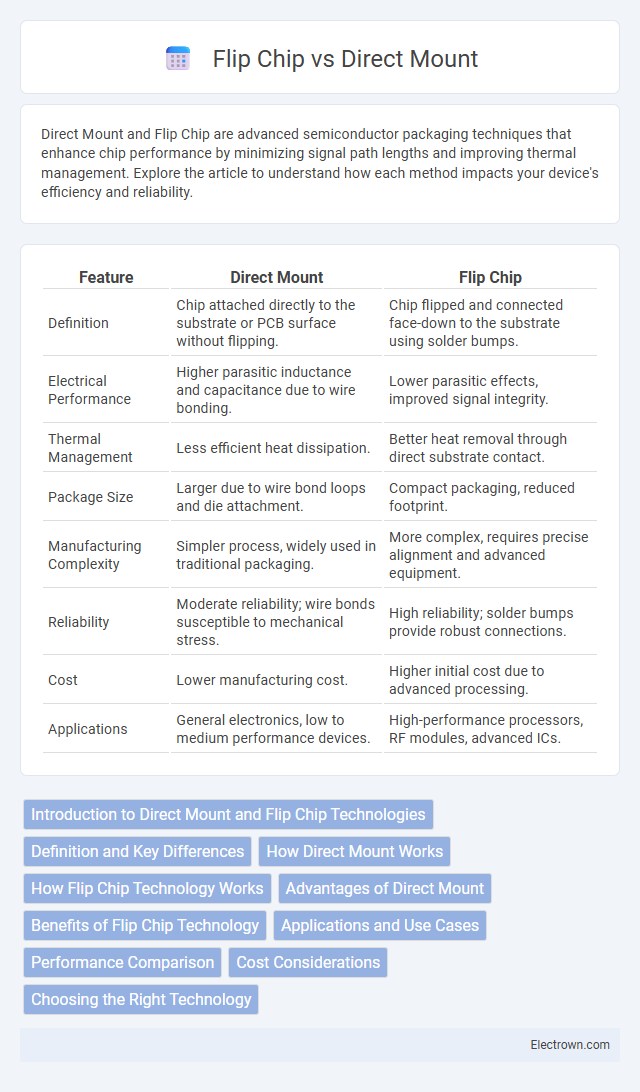
| Feature | Direct Mount | Flip Chip |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chip attached directly to the substrate or PCB surface without flipping. | Chip flipped and connected face-down to the substrate using solder bumps. |
| Electrical Performance | Higher parasitic inductance and capacitance due to wire bonding. | Lower parasitic effects, improved signal integrity. |
| Thermal Management | Less efficient heat dissipation. | Better heat removal through direct substrate contact. |
| Package Size | Larger due to wire bond loops and die attachment. | Compact packaging, reduced footprint. |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simpler process, widely used in traditional packaging. | More complex, requires precise alignment and advanced equipment. |
| Reliability | Moderate reliability; wire bonds susceptible to mechanical stress. | High reliability; solder bumps provide robust connections. |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost. | Higher initial cost due to advanced processing. |
| Applications | General electronics, low to medium performance devices. | High-performance processors, RF modules, advanced ICs. |
Introduction to Direct Mount and Flip Chip Technologies
Direct Mount technology involves attaching semiconductor devices directly onto the substrate with wire bonds, offering robust mechanical support and reliable electrical connections. Flip Chip technology flips the die to connect solder bumps directly to the substrate, minimizing signal path lengths and improving electrical performance. Both methods optimize device integration in advanced microelectronics, with Flip Chip favored for high-frequency and high-density applications due to its superior thermal and electrical characteristics.
Definition and Key Differences
Direct Mount involves attaching semiconductor devices directly onto printed circuit boards using soldering techniques, ensuring a robust mechanical and electrical connection. Flip Chip technology places the chip face-down with solder bumps connecting it to the substrate, enabling shorter interconnects and improved electrical performance. Your choice depends on factors like device size, thermal management, and signal integrity requirements.
How Direct Mount Works
Direct Mount technology involves attaching semiconductor devices directly onto a substrate or printed circuit board (PCB) without using traditional wire bonding, enhancing electrical performance and thermal conductivity. This method improves signal integrity and minimizes parasitic inductance by establishing a shorter, more efficient electrical path. Your device benefits from increased reliability and higher operational speeds due to the precise and robust physical connection enabled by Direct Mount processes.
How Flip Chip Technology Works
Flip Chip technology works by placing the semiconductor die face down on the substrate, using tiny solder bumps to create electrical connections directly between the chip and the circuit board. This method reduces signal path length, improves electrical performance, and enhances heat dissipation compared to Direct Mount techniques. Your devices benefit from increased reliability and miniaturization due to the efficient layout and reduced parasitic inductance in Flip Chip assemblies.
Advantages of Direct Mount
Direct mount technology enhances thermal performance by providing a shorter heat conduction path compared to flip chip, allowing more efficient heat dissipation. This method simplifies assembly processes and reduces overall manufacturing costs by minimizing the need for complex underfill materials and additional interconnect layers. Your electronic devices benefit from improved reliability and potentially longer lifespan due to the robust mechanical attachment offered by direct mount techniques.
Benefits of Flip Chip Technology
Flip chip technology offers superior electrical performance due to shorter interconnect lengths, resulting in reduced inductance and resistance. It enables higher input/output (I/O) densities, allowing more connections per unit area compared to direct mount methods. Enhanced thermal management and improved mechanical reliability are also key benefits, supporting advanced electronic applications demanding miniaturization and high-speed operation.
Applications and Use Cases
Direct mount technology is widely used in applications requiring strong mechanical stability and efficient thermal management, such as LED lighting, power modules, and automotive electronics. Flip chip mounting excels in high-performance semiconductor devices like microprocessors and mobile chips, providing superior electrical performance and miniaturization due to shorter interconnects. Both methods are pivotal in consumer electronics, medical devices, and telecommunications, with the choice depending on specific requirements for heat dissipation, signal integrity, and space constraints.
Performance Comparison
Direct Mount technology offers improved thermal management and electrical performance by reducing parasitic inductance and capacitance compared to Flip Chip designs. Flip Chip provides higher interconnect density and shorter signal paths, resulting in superior high-frequency performance and enhanced signal integrity for advanced semiconductor applications. Each technology optimizes performance metrics differently, with Direct Mount excelling in heat dissipation and Flip Chip leading in miniaturization and speed.
Cost Considerations
Direct Mount technology typically offers lower initial manufacturing costs due to simpler assembly processes and reduced equipment requirements compared to Flip Chip. Flip Chip, while generally more expensive in terms of materials and precise alignment needed, can provide cost savings in high-volume production by enabling finer pitch connections and improved performance. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves considering factors such as yield rates, testing complexity, and long-term reliability alongside upfront expenses.
Choosing the Right Technology
Choosing between direct mount and flip chip technologies depends on your specific application requirements, including thermal performance, electrical connectivity, and manufacturing cost. Flip chip offers superior electrical performance and better heat dissipation due to its shorter interconnect paths, making it ideal for high-speed or high-power devices. Direct mount is more cost-effective and simpler to assemble, suitable for less demanding applications where budget and ease of manufacturing are primary concerns.
Direct Mount vs Flip Chip Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com