Full-custom design offers unparalleled flexibility and optimization by allowing designers to tailor every transistor and circuit element, resulting in superior performance and efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these approaches impact your project's cost, time, and complexity.
Table of Comparison
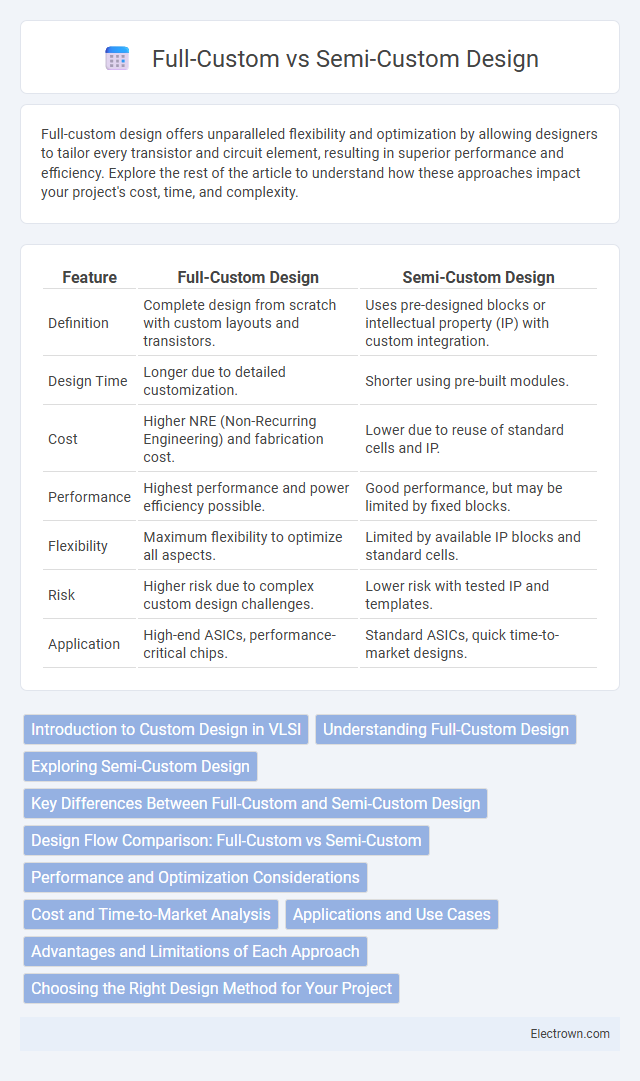
| Feature | Full-Custom Design | Semi-Custom Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete design from scratch with custom layouts and transistors. | Uses pre-designed blocks or intellectual property (IP) with custom integration. |
| Design Time | Longer due to detailed customization. | Shorter using pre-built modules. |
| Cost | Higher NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) and fabrication cost. | Lower due to reuse of standard cells and IP. |
| Performance | Highest performance and power efficiency possible. | Good performance, but may be limited by fixed blocks. |
| Flexibility | Maximum flexibility to optimize all aspects. | Limited by available IP blocks and standard cells. |
| Risk | Higher risk due to complex custom design challenges. | Lower risk with tested IP and templates. |
| Application | High-end ASICs, performance-critical chips. | Standard ASICs, quick time-to-market designs. |
Introduction to Custom Design in VLSI
Full-custom design in VLSI offers maximum control by allowing designers to create every transistor and circuit layout from scratch, optimizing performance and power consumption. Semi-custom design uses pre-designed functional blocks or standard cells, accelerating development and reducing costs while providing moderate customization. Your choice between full-custom and semi-custom approaches impacts design flexibility, manufacturing complexity, and time-to-market in VLSI projects.
Understanding Full-Custom Design
Full-custom design involves creating integrated circuits from the ground up, allowing designers complete control over every transistor and layout element, which maximizes performance and power efficiency. This approach is essential for applications demanding optimized speed, area, and power consumption, such as high-performance processors and specialized ASICs. Despite higher development time and cost, full-custom design delivers unmatched customization and precision compared to semi-custom methods that rely on pre-designed standard cells.
Exploring Semi-Custom Design
Semi-custom design leverages pre-verified standard cells and intellectual property cores, significantly accelerating the development process compared to full-custom design, which requires creating every transistor layout from scratch. This approach lowers overall design costs and reduces time-to-market while maintaining a balance between customization and efficiency. Your project benefits from increased flexibility and faster iteration cycles without sacrificing critical performance metrics in semi-custom design.
Key Differences Between Full-Custom and Semi-Custom Design
Full-Custom design offers complete control over every transistor and layout, enabling maximum performance optimization and power efficiency, while Semi-Custom design uses pre-designed standard cells, reducing development time and costs. Full-Custom projects demand extensive design effort and expertise, ideal for high-performance or specialized applications, whereas Semi-Custom suits faster time-to-market needs with moderate customization. Your choice depends on the balance between design flexibility, manufacturing speed, and budget constraints in your chip development process.
Design Flow Comparison: Full-Custom vs Semi-Custom
Full-custom design involves creating every transistor and circuit element from scratch, resulting in a highly optimized but time-consuming and costly flow with extensive manual intervention and detailed layout verification. Semi-custom design leverages pre-designed logic cells or intellectual property blocks, accelerating the design process through automated place-and-route tools, which reduces development time and costs while sacrificing some optimization and flexibility. The trade-off between full-custom and semi-custom design flows centers on the balance between performance optimization and design turnaround efficiency.
Performance and Optimization Considerations
Full-custom design maximizes performance and optimization by allowing designers to tailor every transistor and routing path, resulting in faster speeds and lower power consumption tailored precisely to your application's requirements. Semi-custom design uses pre-designed standard cells that reduce development time and cost but may limit fine-tuning for peak performance and may lead to less efficient power usage. Choosing full-custom typically benefits high-performance, power-sensitive projects demanding maximum optimization.
Cost and Time-to-Market Analysis
Full-custom design often incurs higher upfront costs and longer development times due to detailed, ground-up engineering tailored for maximum performance and efficiency. Semi-custom design reduces costs and accelerates time-to-market by leveraging pre-designed IP blocks and standardized components, making it ideal for projects with budget or deadline constraints. Your choice between full-custom and semi-custom designs should balance performance needs against financial and schedule limitations.
Applications and Use Cases
Full-custom design excels in high-performance applications such as advanced microprocessors, ASICs for telecommunications, and custom analog circuits where optimized speed, power, and area are critical. Semi-custom design is well-suited for moderate-complexity applications like FPGAs, standard-cell ASICs, and system-on-chip (SoC) solutions, balancing design flexibility and reduced time-to-market. Full-custom is preferred for cutting-edge semiconductor products demanding tailored optimization, while semi-custom supports rapid prototyping and cost-effective mass production.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Full-custom design offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling precise optimization of circuit performance, power consumption, and area, making it ideal for high-performance or specialized applications. However, it demands significant design time, higher costs, and complex verification processes, limiting its feasibility for low-volume production. Semi-custom design accelerates development with reusable standard cells and pre-verified components, reducing time-to-market and overall expenses, though it sacrifices some customization and may face limitations in achieving optimal power and performance metrics.
Choosing the Right Design Method for Your Project
Selecting between full-custom and semi-custom design methods hinges on project requirements, budget, and timeline. Full-custom design offers maximum flexibility and performance optimization, ideal for complex, high-performance applications with ample development time and resources. Semi-custom design accelerates time-to-market and reduces costs by leveraging pre-designed components, making it suitable for projects prioritizing efficiency over granular customization.
Full-Custom vs Semi-Custom Design Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com