CMOS image sensors offer faster processing speeds and lower power consumption compared to CCD sensors, making them ideal for compact and energy-efficient devices. Explore this article to understand how your choice between CMOS and CCD impacts image quality and device performance.
Table of Comparison
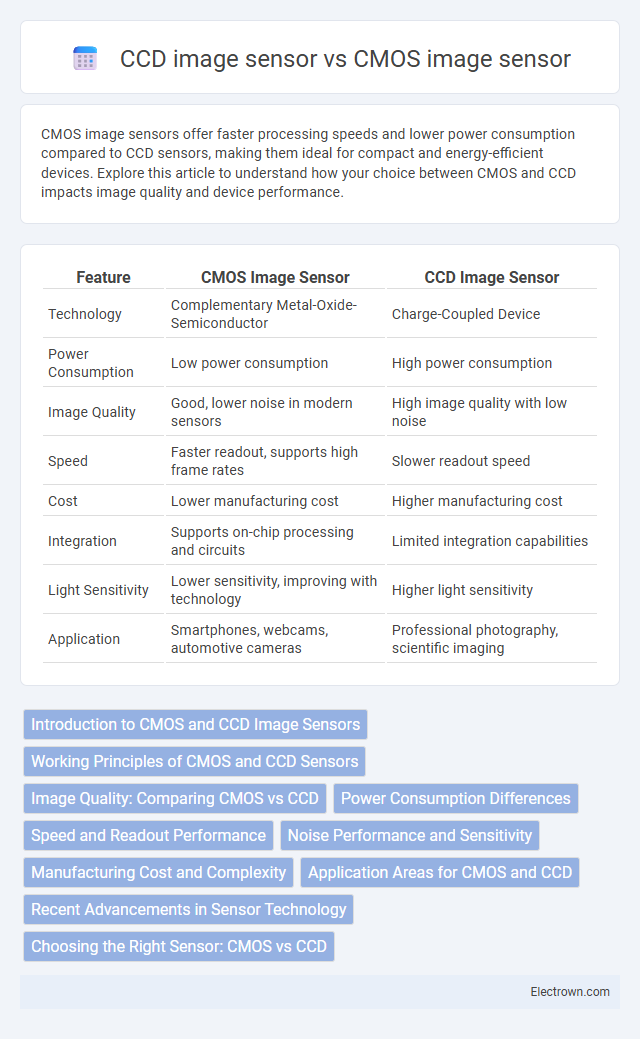
| Feature | CMOS Image Sensor | CCD Image Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor | Charge-Coupled Device |
| Power Consumption | Low power consumption | High power consumption |
| Image Quality | Good, lower noise in modern sensors | High image quality with low noise |
| Speed | Faster readout, supports high frame rates | Slower readout speed |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Integration | Supports on-chip processing and circuits | Limited integration capabilities |
| Light Sensitivity | Lower sensitivity, improving with technology | Higher light sensitivity |
| Application | Smartphones, webcams, automotive cameras | Professional photography, scientific imaging |
Introduction to CMOS and CCD Image Sensors
CMOS image sensors utilize complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor technology to convert light into electrical signals with integrated circuitry, offering benefits like lower power consumption and faster readout speeds. CCD image sensors rely on charge-coupled devices that transfer charge across the sensor to a readout point, providing high image quality and low noise performance. Both sensor technologies are widely used in digital imaging applications, with CMOS favored for consumer electronics and CCD preferred in scientific imaging due to its superior light sensitivity.
Working Principles of CMOS and CCD Sensors
CMOS image sensors operate by converting light into electrical signals using CMOS transistors at each pixel, enabling individual pixel processing and faster readouts. CCD image sensors transfer charge across the chip sequentially to a single output node, resulting in higher image uniformity but slower readout speeds. The distinct architectures influence noise levels, power consumption, and suitability for various imaging applications.
Image Quality: Comparing CMOS vs CCD
CCD image sensors typically offer higher image quality with better light sensitivity and low noise performance, making them ideal for professional photography and scientific applications. CMOS image sensors provide faster readout speeds and lower power consumption, but may exhibit more noise and lower dynamic range compared to CCD sensors. Your choice between CMOS and CCD will impact detail clarity, color accuracy, and overall image performance depending on the specific use case.
Power Consumption Differences
CMOS image sensors consume significantly less power than CCD image sensors due to their on-chip amplification and parallel processing architecture, which reduces energy usage during image capture. CCD sensors require higher power to transfer charges across the chip, resulting in increased consumption and heat generation. This power efficiency advantage makes CMOS sensors more suitable for battery-operated devices and portable imaging applications.
Speed and Readout Performance
CMOS image sensors typically offer faster readout speeds and lower power consumption compared to CCD image sensors, enabling rapid image capture and real-time video processing. CCD sensors, while known for high image quality and low noise due to their charge transfer mechanism, generally have slower readout times that can limit speed performance in high-frame-rate applications. The ability of CMOS sensors to perform random access pixel readout enhances their speed advantage in dynamic imaging scenarios such as high-speed photography and machine vision.
Noise Performance and Sensitivity
CMOS image sensors typically exhibit lower noise performance than CCD sensors due to on-chip noise reduction techniques and individual pixel amplification, enhancing image clarity in low-light conditions. CCD sensors, however, offer superior sensitivity and uniformity by transferring charge across the sensor, resulting in high-quality images with less fixed-pattern noise. The choice between CMOS and CCD sensors heavily depends on the application's demand for noise levels and sensitivity, with CMOS favored in power-sensitive, faster imaging and CCD preferred for high-fidelity, low-noise environments.
Manufacturing Cost and Complexity
CMOS image sensors generally have lower manufacturing costs and complexity compared to CCD image sensors due to their compatibility with standard semiconductor fabrication processes. The integration of multiple functions, such as signal processing on the same chip, reduces the need for additional components and assembly steps. In contrast, CCD sensors require specialized manufacturing techniques and separate components for signal processing, leading to higher production expenses and more intricate design requirements.
Application Areas for CMOS and CCD
CMOS image sensors dominate applications in smartphones, digital cameras, and automotive vision systems due to their low power consumption and high integration capabilities. CCD image sensors are preferred in scientific imaging, medical devices, and professional photography because of their superior image quality and low noise performance. Both sensor types are also used in security cameras, with CMOS favored for cost efficiency and CCD for high-resolution surveillance.
Recent Advancements in Sensor Technology
Recent advancements in CMOS image sensor technology have led to improved low-light performance, higher frame rates, and reduced power consumption compared to traditional CCD image sensors. CMOS sensors now incorporate advanced pixel architectures and on-chip processing, enabling faster data readout and enhanced image quality, which makes them ideal for mobile devices and automotive applications. Your imaging solutions can benefit from these innovations by leveraging CMOS's scalability and integration capabilities for superior efficiency and performance.
Choosing the Right Sensor: CMOS vs CCD
Choosing the right sensor between CMOS and CCD depends on your specific imaging needs, as CMOS sensors offer faster readout speeds, lower power consumption, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for high-speed and portable applications. CCD sensors provide superior image quality with higher sensitivity and lower noise, which is crucial for professional photography and scientific imaging requiring precision. Evaluating your priorities in image quality, speed, and budget will help determine whether a CMOS or CCD sensor better suits your requirements.
CMOS image sensor vs CCD image sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com