VSI (Visual Scene Interpretation) focuses on analyzing visual elements within a scene, while CSI (Crime Scene Investigation) involves the systematic collection and analysis of evidence from crime scenes to solve criminal cases. Discover how understanding the differences between VSI and CSI can enhance your knowledge of forensic and visual analysis techniques by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
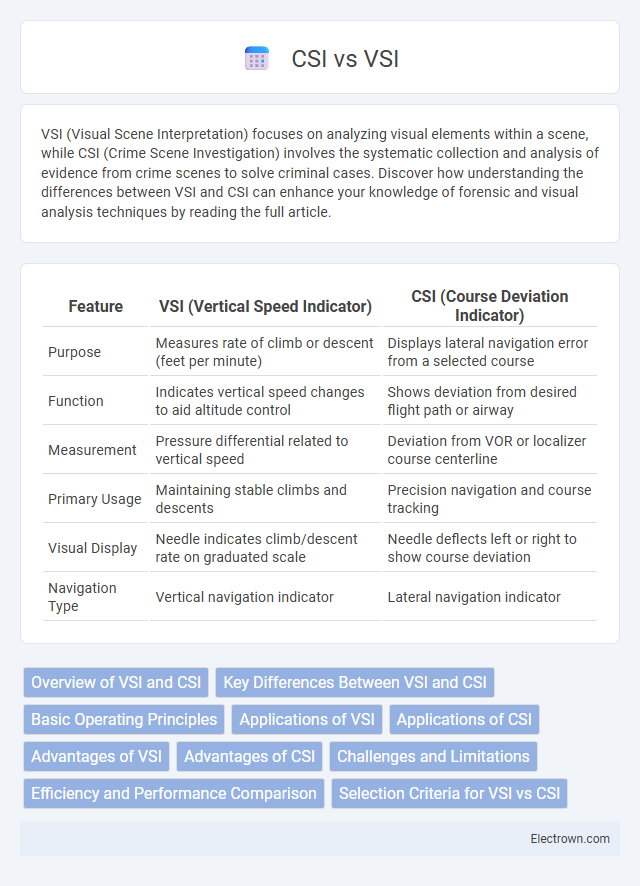
| Feature | VSI (Vertical Speed Indicator) | CSI (Course Deviation Indicator) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures rate of climb or descent (feet per minute) | Displays lateral navigation error from a selected course |
| Function | Indicates vertical speed changes to aid altitude control | Shows deviation from desired flight path or airway |
| Measurement | Pressure differential related to vertical speed | Deviation from VOR or localizer course centerline |
| Primary Usage | Maintaining stable climbs and descents | Precision navigation and course tracking |
| Visual Display | Needle indicates climb/descent rate on graduated scale | Needle deflects left or right to show course deviation |
| Navigation Type | Vertical navigation indicator | Lateral navigation indicator |
Overview of VSI and CSI
Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI) measures the rate of climb or descent in feet per minute, providing pilots with real-time vertical velocity information essential for safe altitude adjustments. Course Deviation Indicator (CDI), often associated with the Course Select Indicator (CSI) in navigation systems, displays lateral position relative to a selected course, aiding in precise enroute navigation and instrument approaches. VSI focuses on vertical movement, while the CSI alerts pilots to horizontal course deviations for accurate flight path maintenance.
Key Differences Between VSI and CSI
VSI (Vertical Speed Indicator) measures the rate of climb or descent in feet per minute, providing real-time vertical velocity data critical for maintaining intended flight profiles. CSI (Course Steering Indicator) displays aircraft position relative to a predetermined navigational course, assisting pilots in lateral guidance for accurate route tracking. While VSI focuses on vertical movement, CSI emphasizes horizontal course adherence, making their functionalities complementary in flight navigation and control.
Basic Operating Principles
VSI (Voltage Source Inverter) operates by converting DC voltage into a controlled AC voltage waveform through switching devices, enabling precise regulation of output voltage and frequency. CSI (Current Source Inverter) maintains a constant input current and generates AC voltage by switching current pulses, ensuring stable current output despite load variations. Understanding your specific application requirements helps determine whether VSI's voltage control or CSI's current control aligns better with your system's basic operating principles.
Applications of VSI
VSI (Vertical Speed Indicator) is essential in aviation for measuring the rate of climb or descent, aiding pilots in maintaining safe altitude changes during flight. Unlike CSI (Cabin Pressure Indicator), which monitors cabin pressure to ensure passenger comfort and safety, VSI provides immediate feedback on vertical velocity, critical during takeoff, landing, and turbulence. Your flight safety depends on accurate VSI readings to prevent stalls or rapid descents, especially in challenging weather conditions.
Applications of CSI
CSI (Channel State Information) is crucial in wireless communication systems for optimizing beamforming, adaptive modulation, and resource allocation to enhance signal quality and network efficiency. Applications of CSI include Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) systems, where precise channel knowledge improves data throughput and reliability. You can leverage CSI for improved connectivity in 5G networks, smart antennas, and real-time channel adaptation to deliver superior user experiences.
Advantages of VSI
VSI (Vertical Speed Indicator) provides precise measurement of an aircraft's rate of climb or descent, enhancing pilot situational awareness during critical flight phases. Unlike CSI (Course Steering Indicator), VSI offers immediate feedback on vertical velocity, supporting safer altitude control and smoother transitions. Your flight experience benefits from VSI's real-time vertical velocity data, which is essential for maintaining optimal glide paths and preventing unintentional altitude deviations.
Advantages of CSI
Channel State Information (CSI) provides real-time, precise knowledge of the wireless channel conditions, enabling adaptive modulation and coding techniques that significantly enhance data throughput and reliability. Unlike Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI), which only measures the aircraft's rate of climb or descent, CSI directly improves communication performance by facilitating beamforming and multi-antenna MIMO systems for better signal quality. This precise channel feedback reduces interference and optimizes resource allocation, making CSI crucial for maximizing spectral efficiency in advanced wireless networks.
Challenges and Limitations
VSI (Vertical Speed Indicator) faces limitations in providing accurate altitude changes during rapid maneuvers or turbulence, often leading to delayed readings. CSI (Customer Satisfaction Index) encounters challenges in capturing real-time customer feedback due to survey fatigue and response biases, affecting data reliability. Both metrics require contextual interpretation to mitigate their inherent constraints and enhance decision-making processes.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
VSI (Vertical Speed Indicator) and CSI (Calibrated Speed Indicator) differ significantly in efficiency and performance during flight operations. VSI measures the rate of climb or descent, offering vital data for maintaining optimal altitude changes with precision, while CSI provides accurate airspeed readings crucial for safe maneuvering and fuel efficiency. Your flight performance improves by integrating both instruments, as they collectively ensure better control and fuel management.
Selection Criteria for VSI vs CSI
Selection criteria for Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI) focus on measuring the aircraft's rate of climb or descent using pressure differential to provide real-time vertical velocity data. In contrast, the Cross-Spectral Index (CSI) selection criteria emphasize assessing cognitive workload or attentional states through EEG signal analysis, prioritizing signal accuracy, noise reduction, and spectral resolution. Choosing between VSI and CSI depends on whether the need is for precise aerodynamic vertical performance metrics or advanced neurophysiological data interpretation.
VSI vs CSI Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com