PFC boost enhances power efficiency and reduces electromagnetic interference compared to a standard boost converter, making it ideal for sensitive electronic applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these technologies impact your device's performance and energy consumption.
Table of Comparison
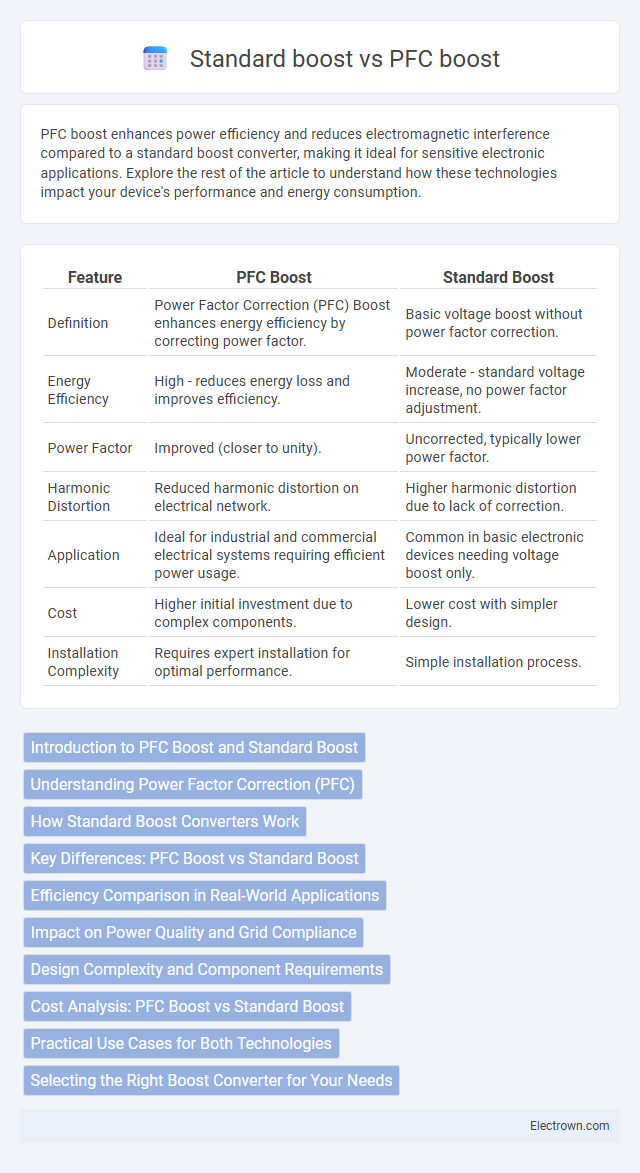
| Feature | PFC Boost | Standard Boost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power Factor Correction (PFC) Boost enhances energy efficiency by correcting power factor. | Basic voltage boost without power factor correction. |
| Energy Efficiency | High - reduces energy loss and improves efficiency. | Moderate - standard voltage increase, no power factor adjustment. |
| Power Factor | Improved (closer to unity). | Uncorrected, typically lower power factor. |
| Harmonic Distortion | Reduced harmonic distortion on electrical network. | Higher harmonic distortion due to lack of correction. |
| Application | Ideal for industrial and commercial electrical systems requiring efficient power usage. | Common in basic electronic devices needing voltage boost only. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to complex components. | Lower cost with simpler design. |
| Installation Complexity | Requires expert installation for optimal performance. | Simple installation process. |
Introduction to PFC Boost and Standard Boost
PFC Boost and Standard Boost are power factor correction techniques designed to improve energy efficiency and reduce electrical losses in electronic devices. PFC Boost uses an inductor and switch to regulate current flow, enhancing power factor closer to unity and reducing harmonic distortion. Your choice between these methods affects the overall performance and compliance with energy standards in power supply systems.
Understanding Power Factor Correction (PFC)
Power Factor Correction (PFC) improves electrical efficiency by aligning voltage and current waveforms, reducing reactive power and minimizing energy losses in power supplies. Standard boost converters elevate DC voltage but lack inherent PFC capabilities, often resulting in lower power factor and increased harmonic distortion. PFC boost circuits integrate voltage boost with power factor correction, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while enhancing overall power quality and reducing energy costs.
How Standard Boost Converters Work
Standard boost converters operate by storing energy in an inductor during the switch-on phase and releasing it to the load at a higher voltage during the switch-off phase. This process uses a transistor as a switch and a diode for current direction, converting a lower DC input voltage to a higher DC output voltage efficiently. Your device benefits from this method by receiving a stable, increased voltage suitable for various electronics without complex power factor correction circuitry.
Key Differences: PFC Boost vs Standard Boost
PFC Boost enhances power factor correction by actively managing reactive power and reducing harmonic distortion, whereas Standard Boost primarily increases voltage output without addressing power quality. PFC Boost systems improve energy efficiency and comply with stringent regulatory standards, while Standard Boost circuits focus on voltage step-up with less emphasis on power factor optimization. The key difference lies in PFC Boost's capability to deliver cleaner, more stable power alongside voltage enhancement, contrasting with the conventional voltage-only emphasis of Standard Boost.
Efficiency Comparison in Real-World Applications
PFC boost converters typically offer higher efficiency than standard boost converters in real-world applications, especially under varying load conditions and input voltage fluctuations. Your systems benefit from improved power factor correction, reducing energy losses and enhancing overall operational performance. Efficiency gains in PFC boost circuits directly translate to lower heat dissipation and extended device lifespan compared to standard boost designs.
Impact on Power Quality and Grid Compliance
PFC boost converters enhance power quality by significantly reducing harmonic distortion and improving power factor, ensuring compliance with stringent grid standards such as IEEE 519. Standard boost converters may cause higher total harmonic distortion (THD) and lower power factor, potentially leading to penalties and non-compliance with power quality regulations. Optimizing your system with a PFC boost solution helps maintain grid stability and meet regulatory requirements efficiently.
Design Complexity and Component Requirements
PFC boost converters require more complex designs with additional inductors, capacitors, and control circuits to achieve power factor correction, increasing component count and cost compared to standard boost converters. Standard boost converters have simpler circuits with fewer components, focusing solely on voltage step-up without the need for power factor regulation. The complexity of PFC boost designs ensures compliance with regulatory standards for harmonic reduction, demanding precise control and increased component tolerance.
Cost Analysis: PFC Boost vs Standard Boost
PFC Boost typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to Standard Boost due to advanced technology and improved energy efficiency, which can reduce long-term operational expenses. Standard Boost systems are generally less expensive initially but may lead to increased electricity consumption and maintenance costs over time. Your choice between PFC Boost and Standard Boost should balance initial investment against potential savings in energy usage and maintenance expenditures.
Practical Use Cases for Both Technologies
PFC boost excels in data center environments and power supplies, enhancing energy efficiency by reducing reactive power and improving power factor correction. Standard boost converters find practical use in portable electronics and battery-powered devices, stepping up voltage levels smoothly for stable operation. Both technologies optimize power management, with PFC boost targeting electrical grid compliance and energy savings, while standard boost converters ensure reliable voltage regulation in compact applications.
Selecting the Right Boost Converter for Your Needs
Choosing between PFC boost and standard boost converters depends on your application's efficiency and power quality requirements. PFC boost converters improve power factor and reduce harmonic distortion, making them ideal for systems requiring compliance with energy regulations and enhanced reliability. Your selection should balance cost, complexity, and performance to ensure optimal voltage regulation andDian Li Xiao Lu for your specific needs.
PFC boost vs Standard boost Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com