SPICE models excel in detailed transistor-level circuit simulation, providing high accuracy for analog and mixed-signal designs, while Verilog-A models offer greater flexibility for behavioral and system-level modeling, enabling faster development and easier integration with digital design flows. Explore the rest of the article to understand which modeling approach best suits your design needs.
Table of Comparison
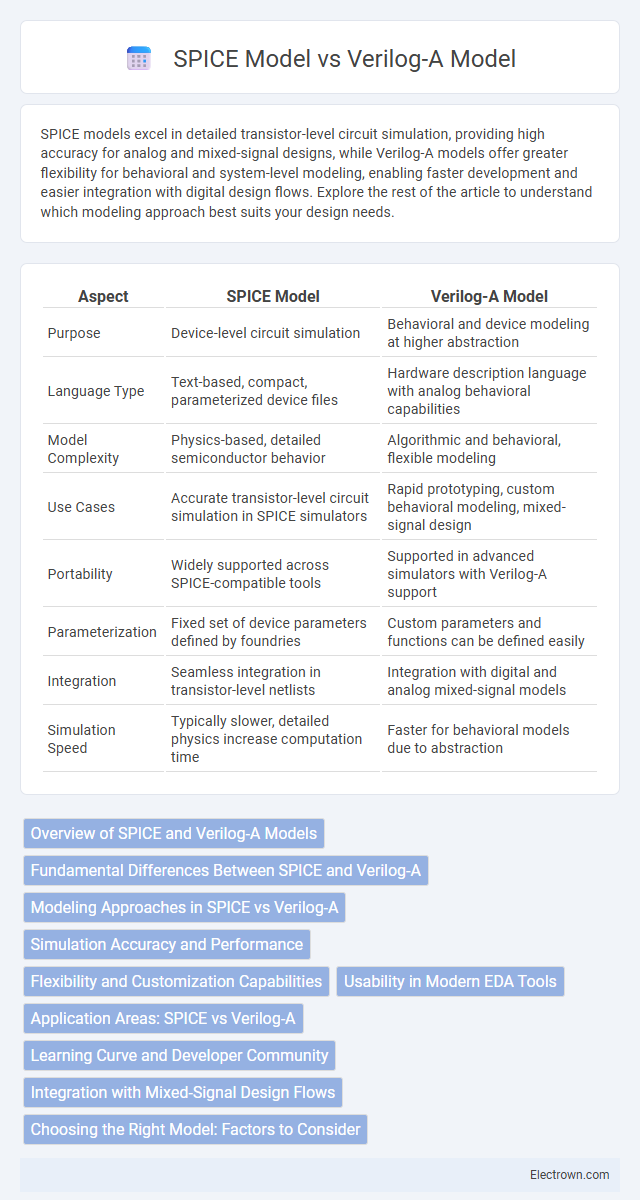
| Aspect | SPICE Model | Verilog-A Model |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Device-level circuit simulation | Behavioral and device modeling at higher abstraction |
| Language Type | Text-based, compact, parameterized device files | Hardware description language with analog behavioral capabilities |
| Model Complexity | Physics-based, detailed semiconductor behavior | Algorithmic and behavioral, flexible modeling |
| Use Cases | Accurate transistor-level circuit simulation in SPICE simulators | Rapid prototyping, custom behavioral modeling, mixed-signal design |
| Portability | Widely supported across SPICE-compatible tools | Supported in advanced simulators with Verilog-A support |
| Parameterization | Fixed set of device parameters defined by foundries | Custom parameters and functions can be defined easily |
| Integration | Seamless integration in transistor-level netlists | Integration with digital and analog mixed-signal models |
| Simulation Speed | Typically slower, detailed physics increase computation time | Faster for behavioral models due to abstraction |
Overview of SPICE and Verilog-A Models
SPICE models provide detailed transistor-level analog circuit simulations based on physical device parameters, enabling accurate electrical behavior prediction under various operating conditions. Verilog-A models offer a higher abstraction level for analog and mixed-signal design, utilizing a hardware description language to describe continuous-time behavior with enhanced flexibility and portability across simulation platforms. Both models serve essential roles in semiconductor device modeling but differ in complexity, simulation speed, and ease of integration into system-level designs.
Fundamental Differences Between SPICE and Verilog-A
SPICE models are behavioral and circuit-level simulations primarily focused on transistor-level device physics with detailed electrical characteristics, while Verilog-A models enable higher abstraction through analog behavioral descriptions suitable for mixed-signal design. SPICE models simulate actual device operation using transistor parameters and compact models, whereas Verilog-A uses algorithmic expressions to represent analog behavior without requiring explicit device physics. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed transistor-level accuracy or flexible, high-level analog modeling for system design.
Modeling Approaches in SPICE vs Verilog-A
SPICE models rely on transistor-level circuit descriptions using predefined device equations and parameter sets to simulate analog behaviors accurately at the electrical level. Verilog-A models employ a behavioral approach, enabling designers to express complex analog phenomena with higher abstraction through continuous-time differential equations and controlled sources. This difference allows Verilog-A to offer greater flexibility and modularity in custom analog and mixed-signal modeling compared to the fixed framework of SPICE models.
Simulation Accuracy and Performance
SPICE models offer high simulation accuracy through device-level detail and physics-based equations, ideal for precise analog circuit analysis. Verilog-A models provide faster simulation performance by abstracting device behavior with behavioral descriptions, enabling efficient large-scale mixed-signal simulations. Balancing accuracy and speed depends on the application, where SPICE excels in detailed device characterization and Verilog-A suits complex system-level designs.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
SPICE models offer detailed transistor-level simulation with high accuracy but limited flexibility, as they rely on predefined device parameters and circuit topologies. Verilog-A models provide superior customization capabilities, allowing you to describe complex analog behaviors with mathematical expressions and behavioral constructs, enabling rapid adaptation to unique or novel device characteristics. Your choice depends on whether precision or flexibility in modeling complex, custom components is the priority.
Usability in Modern EDA Tools
SPICE models offer high accuracy for transistor-level simulations but can be computationally intensive, impacting runtime in complex circuit designs. Verilog-A models provide greater flexibility and faster simulation times, making them more compatible with modern EDA tools that prioritize mixed-signal and system-level verification. Your choice depends on the balance between simulation precision and integration within contemporary design flows.
Application Areas: SPICE vs Verilog-A
SPICE models are primarily used for transistor-level analog circuit simulation and detailed device characterization, excelling in precise electrical behavior analysis. Verilog-A models offer higher abstraction suitable for mixed-signal and system-level simulations, integrating analog behavioral descriptions with digital logic components. SPICE is favored in device engineering and IC verification, while Verilog-A is widely adopted in system architects' design environments and virtual prototyping.
Learning Curve and Developer Community
SPICE models feature a steep learning curve due to their detailed circuit-level simulation capabilities, requiring in-depth understanding of device physics and analog behavior. Verilog-A models offer a more accessible entry point for developers familiar with hardware description languages, supported by a growing community and extensive libraries for mixed-signal design. Your choice between these depends on your project's complexity and the availability of community-driven resources for troubleshooting and development.
Integration with Mixed-Signal Design Flows
SPICE models offer precise transistor-level analog behavior essential for accurate analog circuit simulation but often face challenges in integration efficiency within mixed-signal design flows due to longer simulation times. Verilog-A models provide a higher level of abstraction, enabling seamless integration with digital components in mixed-signal environments and faster simulation convergence. Their compatibility with event-driven simulators enhances co-simulation of analog and digital blocks, making Verilog-A preferable for complex mixed-signal IC design workflows.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right model between SPICE and Verilog-A depends on the complexity of your circuit and simulation goals. SPICE models offer detailed transistor-level accuracy ideal for analog and RF circuit design, while Verilog-A provides behavioral abstraction suitable for system-level and mixed-signal simulations. Your decision should weigh simulation speed, model fidelity, and integration with existing design flows to optimize performance and accuracy.
SPICE model vs Verilog-A model Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com