Negative feedback reduces deviations from a set point, stabilizing systems by counteracting changes, while positive feedback amplifies changes, driving processes toward completion or extremes. Explore the article to understand how these feedback mechanisms influence your body's functions and technological systems.
Table of Comparison
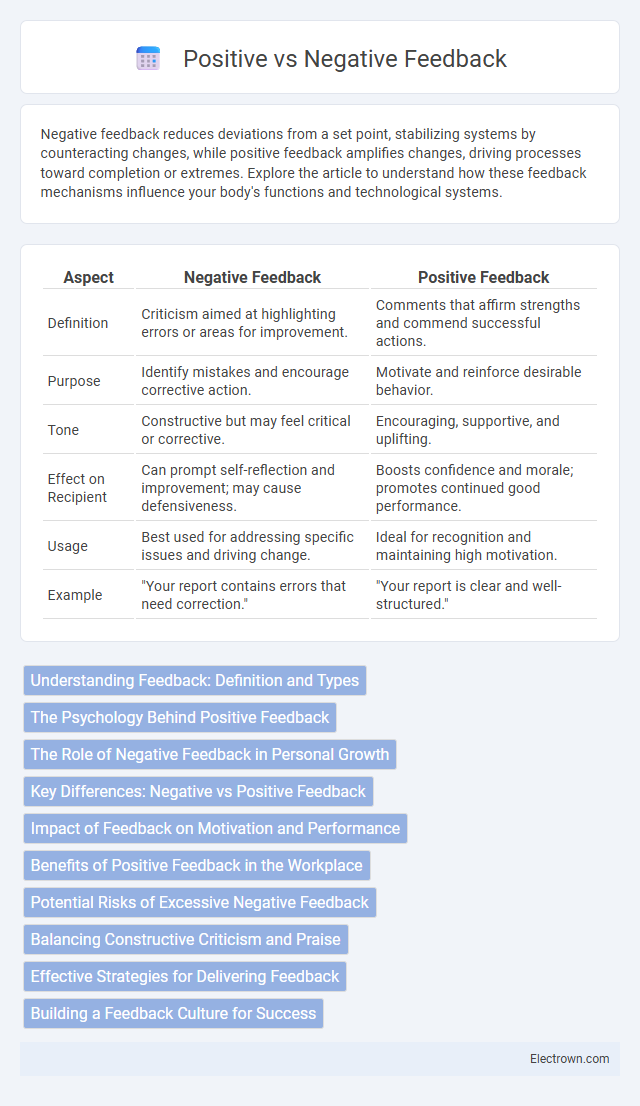
| Aspect | Negative Feedback | Positive Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Criticism aimed at highlighting errors or areas for improvement. | Comments that affirm strengths and commend successful actions. |
| Purpose | Identify mistakes and encourage corrective action. | Motivate and reinforce desirable behavior. |
| Tone | Constructive but may feel critical or corrective. | Encouraging, supportive, and uplifting. |
| Effect on Recipient | Can prompt self-reflection and improvement; may cause defensiveness. | Boosts confidence and morale; promotes continued good performance. |
| Usage | Best used for addressing specific issues and driving change. | Ideal for recognition and maintaining high motivation. |
| Example | "Your report contains errors that need correction." | "Your report is clear and well-structured." |
Understanding Feedback: Definition and Types
Feedback is essential for regulating systems and processes, with two primary types: negative and positive feedback. Negative feedback works to maintain stability by counteracting changes, while positive feedback amplifies deviations, driving rapid shifts or growth. Understanding these mechanisms helps you optimize control in biological, mechanical, or organizational contexts.
The Psychology Behind Positive Feedback
Positive feedback in psychology reinforces desired behaviors by triggering dopamine release, enhancing motivation and learning. It creates a rewarding experience that strengthens neural pathways, making the positive action more likely to recur. Your brain associates success with pleasure, solidifying confidence and promoting growth.
The Role of Negative Feedback in Personal Growth
Negative feedback plays a crucial role in personal growth by identifying areas for improvement and fostering self-awareness. Embracing constructive criticism helps refine skills, build resilience, and enhance decision-making abilities. Your willingness to learn from negative feedback accelerates development and drives continuous progress toward success.
Key Differences: Negative vs Positive Feedback
Negative feedback reduces deviations by counteracting changes, promoting stability and homeostasis in systems such as hormonal regulation. Positive feedback amplifies deviations, enhancing the direction of change to drive processes like blood clotting or childbirth contractions. Key differences include their impact on system behavior: negative feedback maintains equilibrium while positive feedback accelerates responses toward a specific outcome.
Impact of Feedback on Motivation and Performance
Negative feedback can diminish motivation by highlighting errors and shortcomings, often leading to decreased performance and reduced effort. Positive feedback reinforces desired behaviors, boosting self-confidence and enhancing motivation to maintain or improve performance. Balanced feedback combining both types is essential for sustained growth and optimal productivity.
Benefits of Positive Feedback in the Workplace
Positive feedback in the workplace fosters employee motivation, enhances job satisfaction, and boosts productivity by recognizing achievements and reinforcing desired behaviors. It creates a supportive environment that encourages continuous improvement and promotes strong team dynamics. Your ability to effectively deliver positive feedback can lead to increased engagement and a more collaborative organizational culture.
Potential Risks of Excessive Negative Feedback
Excessive negative feedback can lead to decreased employee morale, increased stress levels, and reduced productivity within organizations. Prolonged exposure to critical comments risks fostering a culture of fear and defensiveness, impeding open communication and innovation. Balancing constructive criticism with positive reinforcement is essential to maintain motivation and promote continuous improvement.
Balancing Constructive Criticism and Praise
Balancing constructive criticism and praise involves understanding the roles of negative and positive feedback in personal and professional growth. Negative feedback highlights areas needing improvement, fostering development by addressing mistakes and encouraging problem-solving, while positive feedback reinforces strengths and motivates continued effort. Effective feedback strategies use a mix of both types to build confidence, guide performance, and enhance overall productivity.
Effective Strategies for Delivering Feedback
Effective strategies for delivering feedback involve emphasizing positive reinforcement to motivate and engage individuals, highlighting specific behaviors while maintaining respect and clarity. Negative feedback should be constructive, focusing on actionable improvements without personal criticism, ensuring it supports growth rather than discouragement. Your ability to balance both feedback types with empathy and clear, goal-oriented communication drives meaningful development and performance enhancement.
Building a Feedback Culture for Success
Creating a strong feedback culture hinges on balancing negative and positive feedback to drive continuous improvement and motivation. Positive feedback reinforces strengths and boosts morale, while constructive negative feedback pinpoints areas for growth without diminishing confidence. By embracing this balance, your organization fosters open communication and sustained success.
Negative vs positive feedback Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com