Double diffused MOSFET (DMOS) features a layered fabrication process that enhances device breakdown voltage and ruggedness, making it ideal for high-power and high-frequency applications. Power MOSFETs, designed specifically for switching and amplifying high current at fast speeds, offer low on-resistance and efficient thermal management; explore the rest of the article to understand which MOSFET suits your application best.
Table of Comparison
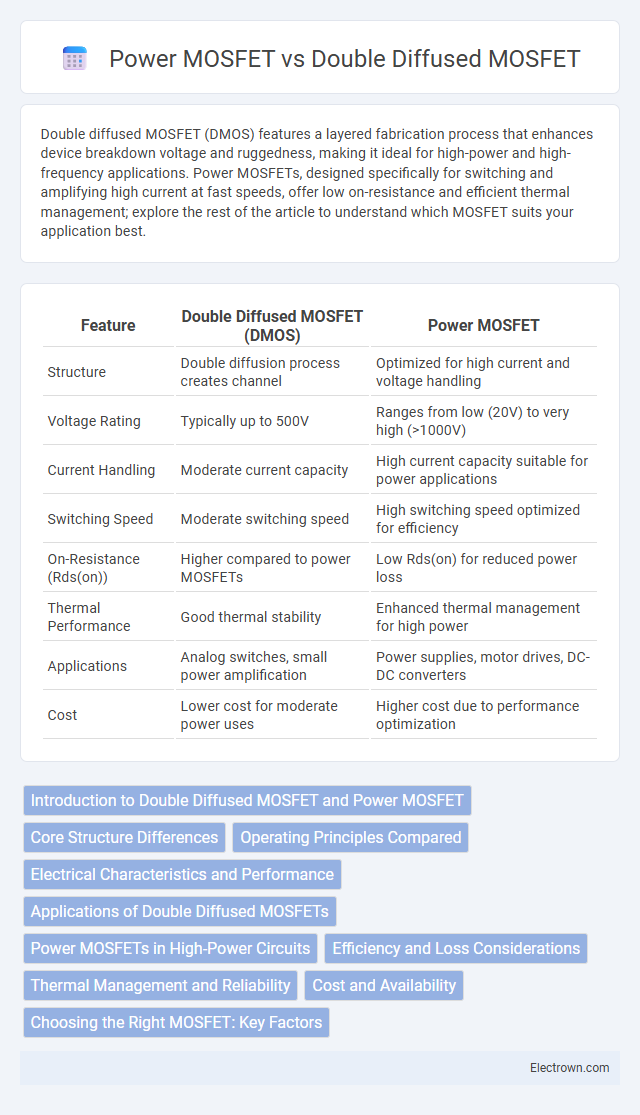
| Feature | Double Diffused MOSFET (DMOS) | Power MOSFET |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Double diffusion process creates channel | Optimized for high current and voltage handling |
| Voltage Rating | Typically up to 500V | Ranges from low (20V) to very high (>1000V) |
| Current Handling | Moderate current capacity | High current capacity suitable for power applications |
| Switching Speed | Moderate switching speed | High switching speed optimized for efficiency |
| On-Resistance (Rds(on)) | Higher compared to power MOSFETs | Low Rds(on) for reduced power loss |
| Thermal Performance | Good thermal stability | Enhanced thermal management for high power |
| Applications | Analog switches, small power amplification | Power supplies, motor drives, DC-DC converters |
| Cost | Lower cost for moderate power uses | Higher cost due to performance optimization |
Introduction to Double Diffused MOSFET and Power MOSFET
Double Diffused MOSFET (DMOS) is a specific type of Power MOSFET designed with a double diffusion process to create the channel region, enhancing device performance in high-voltage and high-current applications. Power MOSFETs generally offer fast switching speeds and low on-resistance, making them ideal for power management in electronics. You can choose between DMOS and standard Power MOSFETs depending on your circuit's voltage, current, and switching requirements.
Core Structure Differences
Double diffused MOSFET (DMOS) features a lateral or vertical double diffusion process creating a more controlled channel region with enhanced doping profiles, enabling better device performance in high-voltage applications. Power MOSFETs typically use a simpler planar or vertical structure designed for efficient current conduction and low on-resistance in power switching scenarios. The core structural difference lies in DMOS's precise double diffusion technique that refines channel control, whereas standard Power MOSFETs prioritize robust, scalable designs optimized for high current handling.
Operating Principles Compared
Double diffused MOSFET (DMOS) features a trench or planar structure with a double diffused channel region allowing precise control of the threshold voltage and improved switching speed. Power MOSFETs, designed for high current and voltage handling, employ a similar MOS gate but optimize the drift region for higher breakdown voltage and lower on-resistance. Your choice depends on whether fast switching and threshold control (DMOS) or power handling and efficiency (Power MOSFET) take priority in the application.
Electrical Characteristics and Performance
Double diffused MOSFETs (DMOS) offer superior electrical characteristics with lower on-resistance (R_DS(on)) and higher current handling capability compared to standard power MOSFETs, enhancing overall efficiency in high-power applications. Their unique double diffusion process creates a well-controlled channel and drift region, resulting in improved switching speed and reduced gate charge, which minimizes power loss during operation. When selecting a power transistor for your design, the choice of DMOS can optimize both performance and thermal management under demanding electrical conditions.
Applications of Double Diffused MOSFETs
Double diffused MOSFETs (DMOS) are widely used in high-power amplifier circuits, radio frequency (RF) applications, and switching regulators due to their high electron mobility and fast switching capabilities. They enable efficient power control in automotive electronics, motor drivers, and audio amplifiers by providing low on-resistance and excellent thermal stability. The DMOS structure supports robust performance in high-voltage and high-frequency applications, distinguishing it from conventional power MOSFETs.
Power MOSFETs in High-Power Circuits
Power MOSFETs are specifically designed for high-power circuits, offering low on-resistance (R_DS(on)) and fast switching speeds to efficiently handle large currents and voltage levels. Double diffused MOSFETs (DMOS) feature a unique fabrication process that creates a precise channel for improved performance but are often optimized for medium to low-power applications. Your choice of a power MOSFET should consider thermal management and switching efficiency to ensure reliability in demanding high-power environments.
Efficiency and Loss Considerations
Double diffused MOSFETs (DDMOSFETs) typically offer lower on-resistance (R_DS(on)), resulting in higher efficiency and reduced conduction losses compared to standard power MOSFETs. Your power conversion efficiency improves as DDMOSFETs minimize switching losses through their optimized doping profiles and faster response times. Selecting a DDMOSFET can significantly reduce heat generation and energy waste in high-current applications.
Thermal Management and Reliability
Double diffused MOSFETs (DMOS) feature enhanced thermal management due to their vertical structure, which provides better heat dissipation across the silicon die compared to traditional Power MOSFETs. The improved thermal conductivity in DMOS devices results in higher reliability under high-current and high-temperature conditions, reducing the risk of thermal runaway. Power MOSFETs, while effective for general switching applications, often require supplementary cooling solutions to maintain similar levels of reliability under heavy thermal stress.
Cost and Availability
Double diffused MOSFETs (DMOS) generally have higher manufacturing complexity, resulting in a slightly higher cost compared to standard power MOSFETs. Power MOSFETs are widely available due to their extensive use in various applications, ensuring lower prices and easier procurement. Your choice should consider budget constraints and the specific performance advantage that DMOS offers in demanding switching or amplification tasks.
Choosing the Right MOSFET: Key Factors
When choosing between Double Diffused MOSFET (DMOS) and Power MOSFET for your application, consider parameters like voltage rating, on-resistance (R_DS(on)), and switching speed. DMOS offers high voltage handling and robustness suitable for high-power switching, while Power MOSFETs excel in low R_DS(on) and fast switching, ideal for efficiency-critical circuits. Evaluating thermal performance and gate charge will help you select the MOSFET that best matches your design's power, frequency, and reliability requirements.
Double diffused MOSFET vs Power MOSFET Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com