Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance stability, longer lifespan, and smaller size compared to electrolytic capacitors, which are generally more cost-effective and have a higher voltage tolerance but shorter durability. To understand which capacitor best suits your electronic projects, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
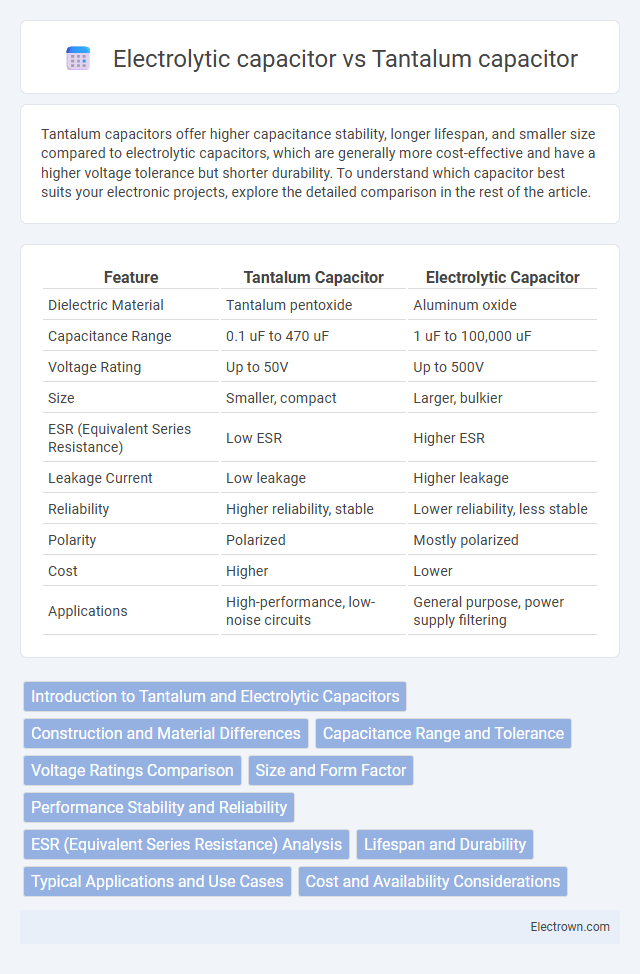
| Feature | Tantalum Capacitor | Electrolytic Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Material | Tantalum pentoxide | Aluminum oxide |
| Capacitance Range | 0.1 uF to 470 uF | 1 uF to 100,000 uF |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 50V | Up to 500V |
| Size | Smaller, compact | Larger, bulkier |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | Low ESR | Higher ESR |
| Leakage Current | Low leakage | Higher leakage |
| Reliability | Higher reliability, stable | Lower reliability, less stable |
| Polarity | Polarized | Mostly polarized |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | High-performance, low-noise circuits | General purpose, power supply filtering |
Introduction to Tantalum and Electrolytic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small size with excellent stability and reliability, making them ideal for precision applications. Electrolytic capacitors provide larger capacitance values and are cost-effective for bulk energy storage in power supplies. Your choice depends on the balance between size, performance, and budget requirements.
Construction and Material Differences
Tantalum capacitors feature a solid manganese dioxide or conductive polymer electrolyte layered on a tantalum metal anode, resulting in a compact, stable structure with high volumetric efficiency. Electrolytic capacitors use an aluminum anode with a liquid or gel electrolyte, providing larger capacitance values but a bulkier design and lower temperature tolerance. Your choice depends on the application's size constraints and performance requirements, as tantalum capacitors offer better reliability and stability, while electrolytic capacitors tend to be more cost-effective for high-capacitance needs.
Capacitance Range and Tolerance
Tantalum capacitors typically offer capacitance values ranging from 0.1uF to 470uF with tight tolerance levels between +-5% and +-10%, making them ideal for precision applications. Electrolytic capacitors provide a broader capacitance range, from 1uF up to 10,000uF or more, but usually have looser tolerances of +-20% or worse. Understanding these differences helps you select the appropriate capacitor type based on your circuit's capacitance requirements and accuracy needs.
Voltage Ratings Comparison
Tantalum capacitors typically offer stable voltage ratings ranging from 4V to 50V, making them ideal for low-voltage applications with high capacitance requirements. Electrolytic capacitors, on the other hand, can handle higher voltage ratings, often up to 450V or more, suitable for power supply filtering and high-voltage circuits. Your choice depends on whether you need higher voltage tolerance or compact size with consistent performance at lower voltages.
Size and Form Factor
Tantalum capacitors offer a smaller size and more compact form factor compared to electrolytic capacitors, making them ideal for applications with limited space. Their stable capacitance and high volumetric efficiency enable miniaturization in portable devices and high-density circuit boards. Electrolytic capacitors tend to be larger and bulkier due to their construction, limiting their use where size constraints are critical.
Performance Stability and Reliability
Tantalum capacitors offer superior performance stability and reliability compared to electrolytic capacitors, maintaining consistent capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR) over extended periods and under varying temperature conditions. Your electronics benefit from tantalum's inherent resistance to leakage and voltage spikes, ensuring stable operation in critical applications. Electrolytic capacitors, while cost-effective, are prone to higher ESR and gradual degradation, which can impact long-term reliability and performance stability.
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) Analysis
Tantalum capacitors exhibit significantly lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to electrolytic capacitors, resulting in better performance in high-frequency applications and improved efficiency in power delivery. Electrolytic capacitors tend to have higher ESR, which can cause increased heat generation and limited lifespan under high ripple current conditions. Understanding ESR differences helps you select the optimal capacitor type for stable and reliable circuit design.
Lifespan and Durability
Tantalum capacitors offer a longer lifespan and higher durability compared to electrolytic capacitors due to their stable oxide layer and solid electrolyte, which resist degradation over time. Electrolytic capacitors typically have shorter lifespans because their liquid electrolyte can evaporate or leak, leading to reduced capacitance and eventual failure. In high-stress applications, tantalum capacitors maintain performance more reliably under temperature fluctuations and electrical stress.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Tantalum capacitors are commonly used in space-sensitive electronics such as smartphones, medical devices, and automotive control systems due to their stable capacitance and reliability at high frequencies. Electrolytic capacitors excel in power supply filtering, audio equipment, and large-scale industrial applications where high capacitance values and cost efficiency are crucial. Your choice depends on the application's size constraints, voltage requirements, and performance needs.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Tantalum capacitors generally have a higher cost due to their specialized materials and manufacturing process, while electrolytic capacitors are more cost-effective and widely available. Electrolytic capacitors offer greater availability in varying capacitance and voltage ratings, making them suitable for mass-market applications. Tantalum capacitors are preferred in space-constrained designs requiring stable performance despite limited availability and premium pricing.
Tantalum capacitor vs Electrolytic capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com