Conductors allow electric current to flow easily due to their free electrons, while insulators resist electrical flow, preventing current from passing through. To understand how these materials impact your daily electronics and safety, continue reading the article.
Table of Comparison
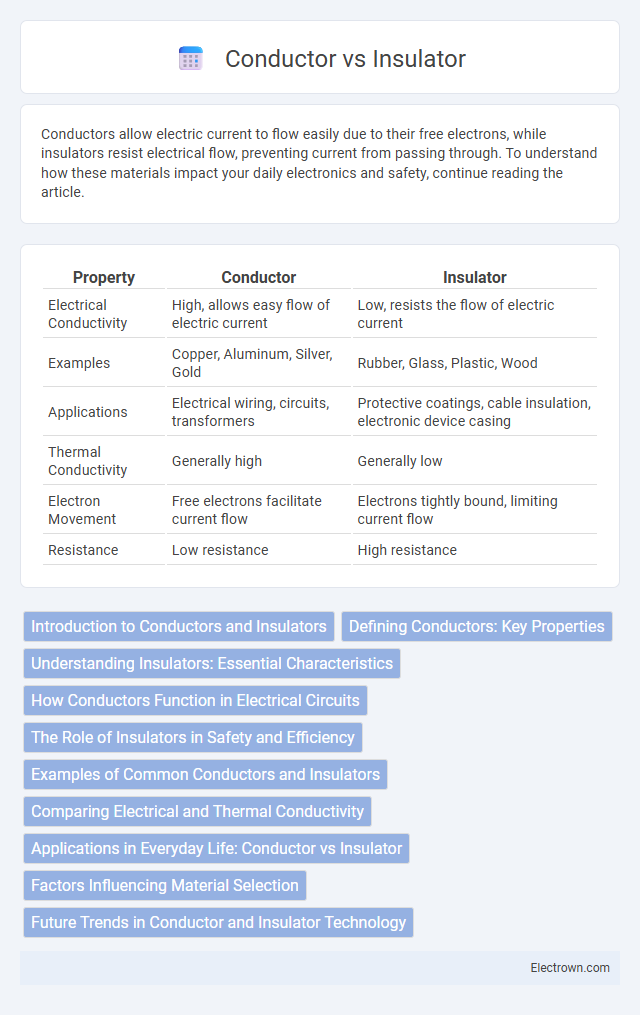
| Property | Conductor | Insulator |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, allows easy flow of electric current | Low, resists the flow of electric current |
| Examples | Copper, Aluminum, Silver, Gold | Rubber, Glass, Plastic, Wood |
| Applications | Electrical wiring, circuits, transformers | Protective coatings, cable insulation, electronic device casing |
| Thermal Conductivity | Generally high | Generally low |
| Electron Movement | Free electrons facilitate current flow | Electrons tightly bound, limiting current flow |
| Resistance | Low resistance | High resistance |
Introduction to Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials like copper and aluminum that allow electric current to flow freely due to their free electrons, making them essential for electrical wiring and circuits. Insulators, such as rubber and glass, restrict electric current flow by lacking free electrons, ensuring safety by preventing unwanted current transfer. Understanding the difference between your conductor and insulator materials is vital for designing effective electrical systems and protecting equipment.
Defining Conductors: Key Properties
Conductors are materials characterized by their ability to allow the free flow of electric current due to the presence of loosely bound electrons in their atomic structure. Metals like copper and aluminum serve as excellent examples of conductors, featuring high electrical conductivity and low resistance. Understanding these key properties helps you select suitable materials for efficient electrical and electronic applications.
Understanding Insulators: Essential Characteristics
Insulators are materials that inhibit the flow of electric current due to their high electrical resistance and tightly bound electrons. Common insulators include rubber, glass, and plastic, which prevent energy loss and protect against electric shock. Their essential characteristic is the ability to block electron movement, making them crucial for electrical safety and circuit integrity.
How Conductors Function in Electrical Circuits
Conductors function in electrical circuits by allowing free flow of electric current due to their abundant free electrons, which move easily through the material's atomic structure. Metals like copper and aluminum serve as prime examples, facilitating efficient transmission of electricity with minimal resistance. Their low resistivity ensures rapid and safe conduction, making them essential in wiring and circuit components.
The Role of Insulators in Safety and Efficiency
Insulators play a crucial role in safety by preventing the flow of electric current, protecting both people and equipment from electric shocks and short circuits. Their ability to restrict current enhances the efficiency of electrical systems by minimizing energy loss and maintaining the integrity of conductive pathways. Understanding the function of insulators helps you ensure safer and more efficient management of electrical circuits.
Examples of Common Conductors and Insulators
Copper, aluminum, gold, and silver are common conductors widely used in electrical wiring and electronic components due to their high electrical conductivity. Common insulators include rubber, glass, plastic, and wood, which are utilized to prevent the flow of electric current and protect against electric shocks. Conductors enable efficient transmission of electricity, while insulators ensure safety and prevent energy loss.
Comparing Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Conductors, such as copper and aluminum, exhibit high electrical and thermal conductivity due to the free movement of electrons, enabling efficient transfer of both electric current and heat. Insulators, including rubber and glass, have tightly bound electrons, resulting in very low electrical conductivity and poor thermal conductivity, effectively preventing the flow of electricity and minimizing heat transfer. This fundamental difference makes conductors ideal for wiring and heat dissipation, whereas insulators are essential for electrical safety and thermal insulation applications.
Applications in Everyday Life: Conductor vs Insulator
Conductors like copper and aluminum enable efficient electrical wiring in homes and electronic devices due to their low resistance, ensuring safe and effective energy transfer. Insulators such as rubber, glass, and plastic protect users by preventing unwanted electrical flow, making them essential for coating wires and manufacturing household appliances. The strategic combination of conductors and insulators is crucial for optimizing electrical safety and performance in everyday technology and infrastructure.
Factors Influencing Material Selection
Material selection between conductors and insulators depends on electrical conductivity, thermal resistance, and application-specific requirements such as safety standards and environmental conditions. Metals like copper and aluminum are preferred for conductors due to their high conductivity and durability, while materials like rubber, glass, and ceramics are chosen as insulators for their ability to prevent current flow and withstand high voltages. Cost, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance also play crucial roles in determining the appropriate material in electrical and electronic applications.
Future Trends in Conductor and Insulator Technology
Future trends in conductor technology highlight the development of graphene and carbon nanotube-based materials, which promise higher conductivity and flexibility for electronics and energy transmission. Insulator advancements emphasize the creation of nanocomposite materials that enhance thermal stability and dielectric strength, essential for next-generation electronic devices and high-voltage applications. Innovations in biodegradable and eco-friendly insulators also align with growing environmental sustainability goals in electrical engineering.
conductor vs insulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com