Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and better frequency characteristics compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, which are more cost-effective and provide higher voltage ratings but larger size. Explore this article to understand which capacitor best suits Your electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
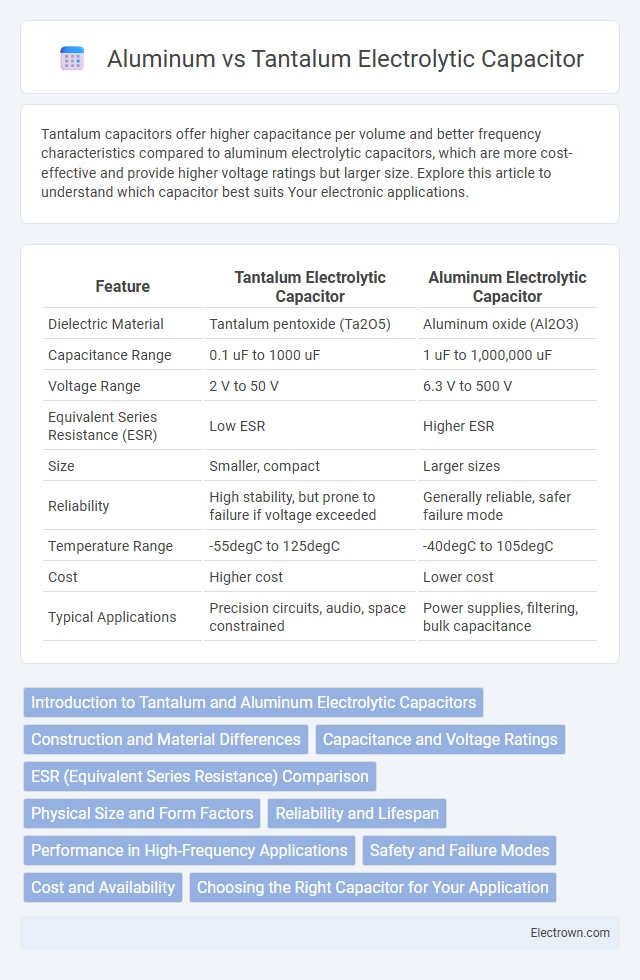
| Feature | Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitor | Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Material | Tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Capacitance Range | 0.1 uF to 1000 uF | 1 uF to 1,000,000 uF |
| Voltage Range | 2 V to 50 V | 6.3 V to 500 V |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Low ESR | Higher ESR |
| Size | Smaller, compact | Larger sizes |
| Reliability | High stability, but prone to failure if voltage exceeded | Generally reliable, safer failure mode |
| Temperature Range | -55degC to 125degC | -40degC to 105degC |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Typical Applications | Precision circuits, audio, space constrained | Power supplies, filtering, bulk capacitance |
Introduction to Tantalum and Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
Tantalum and aluminum electrolytic capacitors serve distinct roles in electronic circuits due to their unique material properties and construction. Tantalum capacitors feature a tantalum metal anode with a solid electrolyte, offering superior stability, lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), and higher volumetric efficiency compared to aluminum capacitors. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors utilize an aluminum foil anode with a liquid electrolyte, making them more cost-effective and suitable for high capacitance values but generally less stable under varying temperatures and frequencies.
Construction and Material Differences
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors use a tantalum metal anode with a manganese dioxide or polymer cathode, offering high capacitance in a small volume and excellent stability. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors consist of an aluminum foil anode, an aluminum oxide dielectric layer formed by electrochemical oxidation, and a liquid or solid electrolyte, providing cost-effective and high-voltage options. Understanding these construction and material differences helps you select the right capacitor based on performance, size, and reliability requirements.
Capacitance and Voltage Ratings
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values in smaller volumes compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, making them suitable for compact electronic designs. Voltage ratings for tantalum capacitors generally range from 2V to 50V, while aluminum electrolytic capacitors support a broader voltage spectrum, often from 6.3V up to 450V or higher. The voltage stability of tantalum capacitors enhances performance in sensitive circuits, whereas aluminum capacitors are preferred for high-voltage, high-ripple current applications.
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) Comparison
Tantalum capacitors typically exhibit lower ESR values compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, resulting in improved performance in high-frequency applications and better efficiency in power supply filtering. The reduced ESR in tantalum capacitors helps minimize heat generation and voltage drops, enhancing reliability and lifespan under demanding conditions. Understanding this difference can help you select the optimal capacitor type for your circuit's stability and efficiency requirements.
Physical Size and Form Factors
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors typically offer smaller physical sizes and more compact form factors compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, making them ideal for applications with limited space requirements. Their solid electrolyte design enables stable capacitance in miniature packages like surface-mount device (SMD) formats, whereas aluminum capacitors often require larger cylindrical or box shapes due to liquid electrolyte content. The difference in volume efficiency allows tantalum capacitors to deliver higher capacitance per unit volume, contributing to denser circuit board layouts.
Reliability and Lifespan
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors offer superior reliability and a longer lifespan compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, thanks to their stable oxide layer and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR). Aluminum capacitors are more prone to drying out and electrolyte leakage, which can significantly reduce their operational durability and performance over time. Choosing tantalum capacitors enhances Your circuit's stability in demanding applications where longevity and consistent performance are critical.
Performance in High-Frequency Applications
Tantalum capacitors exhibit superior performance in high-frequency applications due to their low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and stable capacitance over a wide frequency range. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors tend to have higher ESR and inductance, which can degrade signal integrity and reduce filtering effectiveness at elevated frequencies. The lower noise and better frequency response of tantalum capacitors make them ideal for RF circuits and high-speed digital applications requiring precise waveform stability.
Safety and Failure Modes
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors exhibit higher safety risks due to their tendency to fail short-circuit under voltage spikes or excessive ripple current, often resulting in thermal runaway or combustion. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors predominantly fail open-circuit, which reduces catastrophic consequences but can cause circuit malfunction or degradation over time. Proper derating and quality control are essential for mitigating failure modes in both capacitor types, with tantalum capacitors requiring stricter design considerations to ensure operational safety.
Cost and Availability
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors generally have higher costs due to the expensive tantalum material and complex manufacturing process compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, which use abundant aluminum foil, making them more affordable. Availability of aluminum capacitors is widespread worldwide, supported by a large number of manufacturers and stable supply chains, whereas tantalum capacitors face supply constraints influenced by limited tantalum ore sources and geopolitical factors. Overall, aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer better cost-efficiency and broader market availability for high-volume production needs.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your Application
Tantalum capacitors deliver higher capacitance per volume and superior stability under temperature changes, making them ideal for space-constrained or precision electronics applications. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer larger capacitance values and better transient response at a lower cost, suitable for power supply smoothing and audio equipment. To optimize your circuit performance, consider factors like voltage rating, lifespan, ripple current, and frequency response when choosing between tantalum and aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
Tantalum vs aluminum electrolytic capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com