FR4 offers cost-effective, reliable performance for standard electronic applications, while ceramic substrates provide superior thermal conductivity and durability for high-power or high-frequency devices. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits your specific project needs.
Table of Comparison
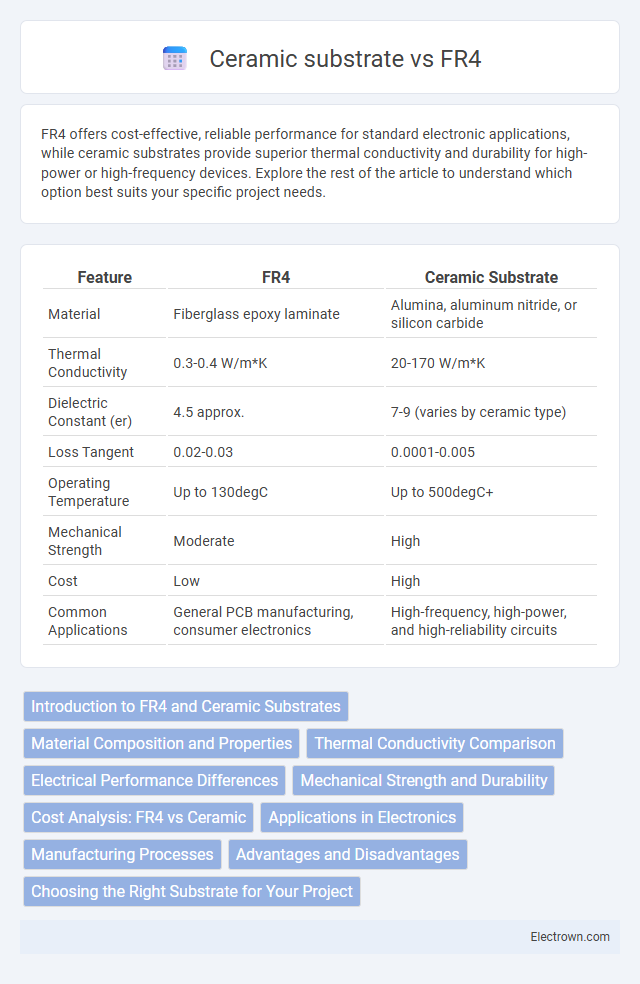
| Feature | FR4 | Ceramic Substrate |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Fiberglass epoxy laminate | Alumina, aluminum nitride, or silicon carbide |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.3-0.4 W/m*K | 20-170 W/m*K |
| Dielectric Constant (er) | 4.5 approx. | 7-9 (varies by ceramic type) |
| Loss Tangent | 0.02-0.03 | 0.0001-0.005 |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 130degC | Up to 500degC+ |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Common Applications | General PCB manufacturing, consumer electronics | High-frequency, high-power, and high-reliability circuits |
Introduction to FR4 and Ceramic Substrates
FR4 is a widely used fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate that offers affordable mechanical strength and electrical insulation for printed circuit boards (PCBs). Ceramic substrates, typically made from materials like alumina or aluminum nitride, provide superior thermal conductivity and excellent electrical performance suited for high-frequency and high-power applications. Both substrates serve distinct roles in electronics, with FR4 favored for cost-effective general use, while ceramics excel in demanding environments requiring enhanced heat dissipation and signal integrity.
Material Composition and Properties
FR4 is a composite material made of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder, known for its good mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and flame resistance at a relatively low cost. Ceramic substrates, typically composed of aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride, offer superior thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength, and excellent electrical insulation, making them ideal for high-frequency and high-power applications. The dielectric constant of FR4 ranges from 4.3 to 4.8, while ceramic substrates have lower and more stable dielectric constants between 8 and 9, improving signal integrity in advanced electronics.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
FR4 substrates have a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.3-0.4 W/m*K, making them less effective at dissipating heat compared to ceramic substrates, which typically exhibit thermal conductivities ranging from 20 to 150 W/m*K depending on the ceramic type. High thermal conductivity in ceramic substrates enhances heat dissipation, reducing thermal stress and improving the reliability of your electronic components in high-power or high-frequency applications. Selecting a ceramic substrate over FR4 can significantly improve thermal management and overall device performance in demanding environments.
Electrical Performance Differences
FR4 and ceramic substrates differ significantly in electrical performance, with FR4 offering moderate dielectric constant values around 4.5 suitable for general-purpose PCBs, while ceramic substrates provide much lower dielectric constants often below 10, enabling higher signal speed and reduced loss. Ceramic substrates exhibit superior thermal conductivity and insulation properties, minimizing signal interference and crosstalk in high-frequency applications compared to FR4. Your choice between these materials impacts impedance control, signal integrity, and overall circuit reliability in advanced electronics.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
FR4 offers good mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for general-purpose PCB applications where moderate durability is required. Ceramic substrates provide superior mechanical strength and excellent thermal stability, with high resistance to wear and environmental stress, ideal for high-reliability and extreme conditions. The inherent brittleness of ceramic materials can reduce impact resistance compared to FR4, but their durability under thermal cycling and mechanical stress surpasses that of FR4.
Cost Analysis: FR4 vs Ceramic
FR4 substrates generally offer a lower cost solution compared to ceramic substrates due to their widespread availability and simpler manufacturing processes. Ceramic substrates, while more expensive, provide superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation critical for high-performance applications. Your choice should balance budget constraints and performance requirements to optimize overall system efficiency.
Applications in Electronics
FR4 substrates are widely used in general electronics due to their cost-effectiveness and good mechanical strength, making them ideal for printed circuit boards in consumer devices and industrial equipment. Ceramic substrates offer superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, which is crucial for high-frequency applications, power electronics, and automotive sensors where heat dissipation and signal integrity are critical. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize affordability and versatility with FR4 or enhanced performance and reliability with ceramic materials in demanding electronic environments.
Manufacturing Processes
FR4 substrates are manufactured using woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin, followed by layering and curing to create a rigid, flame-retardant board. Ceramic substrates require high-temperature sintering of ceramic powders, often alumina or aluminum nitride, resulting in superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. Your choice between FR4 and ceramic depends on manufacturing complexity and the application's thermal and electrical performance requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages
FR4 substrates offer cost-effective and widely available solutions with good mechanical strength and electrical insulation, ideal for standard PCB applications. Ceramic substrates provide superior thermal conductivity, higher frequency performance, and excellent dimensional stability but come at a higher cost and increased manufacturing complexity. Your choice depends on the critical balance between performance requirements and budget constraints in your electronic design.
Choosing the Right Substrate for Your Project
FR4 offers a cost-effective, widely used substrate with good mechanical strength and electrical insulation, making it ideal for general-purpose PCBs. Ceramic substrates provide superior thermal conductivity, excellent high-frequency performance, and greater durability under extreme conditions, suitable for high-power and high-temperature applications. Selecting between FR4 and ceramic depends on project requirements including thermal management, electrical properties, and budget constraints.
FR4 vs ceramic substrate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com