Tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors differ primarily in their dielectric materials, with tantalum offering higher capacitance and stability, whereas niobium oxide provides improved safety and cost-effectiveness. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which capacitor best suits Your electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
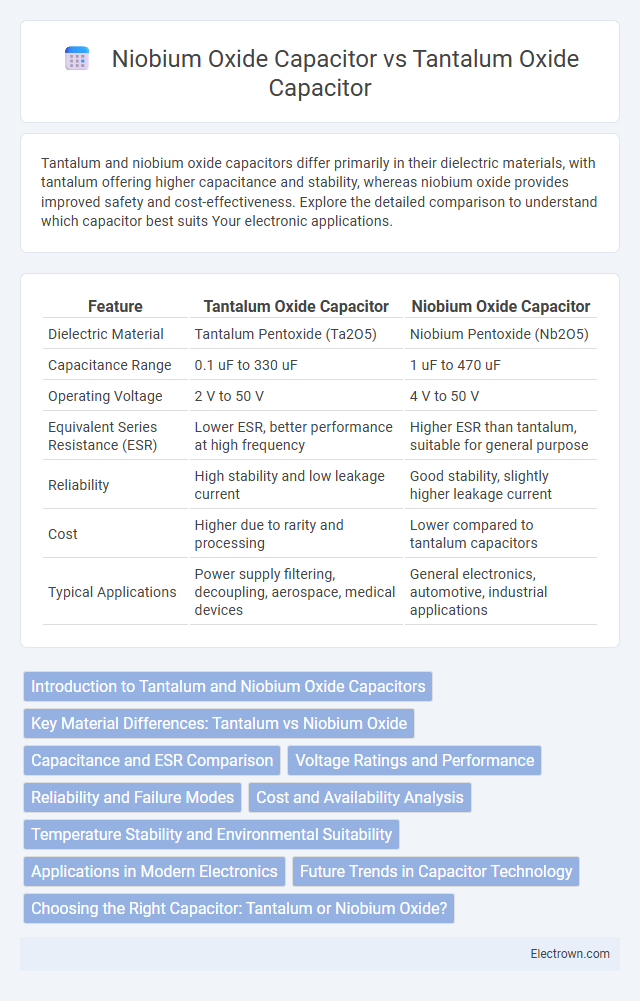
| Feature | Tantalum Oxide Capacitor | Niobium Oxide Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Material | Tantalum Pentoxide (Ta2O5) | Niobium Pentoxide (Nb2O5) |
| Capacitance Range | 0.1 uF to 330 uF | 1 uF to 470 uF |
| Operating Voltage | 2 V to 50 V | 4 V to 50 V |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Lower ESR, better performance at high frequency | Higher ESR than tantalum, suitable for general purpose |
| Reliability | High stability and low leakage current | Good stability, slightly higher leakage current |
| Cost | Higher due to rarity and processing | Lower compared to tantalum capacitors |
| Typical Applications | Power supply filtering, decoupling, aerospace, medical devices | General electronics, automotive, industrial applications |
Introduction to Tantalum and Niobium Oxide Capacitors
Tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors are key components in electronic circuits, valued for their high capacitance and reliability in compact sizes. Tantalum capacitors offer stable performance with high volumetric efficiency, making them suitable for demanding applications like aerospace and medical devices. Niobium oxide capacitors provide comparable advantages with improved safety and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), supporting high-frequency and high-temperature operations.
Key Material Differences: Tantalum vs Niobium Oxide
Tantalum capacitors utilize tantalum pentoxide as the dielectric, offering high capacitance per volume and excellent long-term stability, making them ideal for space-constrained and high-reliability applications. Niobium oxide capacitors use niobium oxide dielectric, providing comparable capacitance with improved environmental compliance and enhanced safety due to lower risk of catastrophic failure. Your choice between tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors should consider factors like dielectric performance, thermal stability, and application-specific reliability needs.
Capacitance and ESR Comparison
Tantalum oxide capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values per volume compared to niobium oxide capacitors, making them suitable for space-constrained applications. Niobium oxide capacitors generally exhibit lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), enhancing their performance in high-frequency and high-ripple current environments. The trade-off between capacitance density and ESR should be considered when selecting between tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors for optimized circuit performance.
Voltage Ratings and Performance
Tantalum oxide capacitors typically offer higher voltage ratings, ranging from 6.3V to 125V, while niobium oxide capacitors generally operate within 6.3V to 50V. Tantalum capacitors deliver excellent performance in stable capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), making them suitable for high-reliability applications. Your choice depends on voltage requirements and performance needs, as niobium oxide capacitors provide better safety margins due to their stable oxide layer under stress.
Reliability and Failure Modes
Tantalum oxide capacitors offer high reliability with stable capacitance and low leakage current but are prone to catastrophic failure due to dielectric breakdown if voltage spikes occur. Niobium oxide capacitors exhibit improved failure tolerance, often failing in a safe, self-healing mode, which enhances overall reliability in harsh conditions. Your choice between these capacitors should consider the specific application's voltage stability and tolerance for failure risk.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Tantalum oxide capacitors generally have higher costs due to the rarity of tantalum and processing complexities, with prices fluctuating sharply based on geopolitical supply constraints primarily from the Democratic Republic of Congo. Niobium oxide capacitors offer a more cost-effective alternative as niobium is more abundant and evenly distributed globally, ensuring steadier pricing and availability. The stable supply chain of niobium oxide capacitors makes them preferable in high-volume production, where cost and long-term availability are critical factors.
Temperature Stability and Environmental Suitability
Tantalum oxide capacitors exhibit excellent temperature stability with a wide operating range from -55degC to +125degC, making them suitable for harsh environments and maintaining performance under thermal stress. Niobium oxide capacitors typically offer a similar temperature range but are often preferred in applications requiring enhanced moisture resistance and lower ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance), which improves environmental suitability in humid or corrosive conditions. Choosing between these capacitors depends on your specific temperature stability needs and the environmental challenges of your project.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors are essential components in modern electronics due to their high capacitance and stability under varying temperatures and frequencies. Tantalum capacitors are widely used in smartphones, medical devices, and automotive electronics where reliability and compact size are crucial, while niobium oxide capacitors offer enhanced voltage tolerance and higher energy density, making them ideal for power supply circuits and high-performance computing applications. Both capacitor types contribute significantly to energy-efficient designs and miniaturization trends in advanced consumer electronics and industrial systems.
Future Trends in Capacitor Technology
Tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors are rapidly evolving with advancements in miniaturization and higher capacitance density, addressing the growing demands of wearable and IoT devices. Innovations in electrolyte formulation and anodization processes improve reliability and temperature stability, enabling their use in harsh environments. Emerging trends also emphasize environmentally friendly materials and enhanced energy efficiency to support sustainable electronic designs.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: Tantalum or Niobium Oxide?
Choosing between tantalum and niobium oxide capacitors depends on your application's performance and reliability needs; tantalum capacitors offer high volumetric efficiency and stable electrical characteristics under temperature variations. Niobium oxide capacitors provide improved safety with lower risk of catastrophic failure and better tolerance to voltage surges, making them ideal for sensitive electronics requiring enhanced reliability. Assess your circuit's voltage, capacitance, and safety requirements to determine whether the superior energy density of tantalum or the robust failure mode of niobium oxide is more suitable for your design.
tantalum vs niobium oxide capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com