Silver nanoparticle ink offers superior electrical conductivity and faster drying times compared to carbon-based ink, making it ideal for high-performance printed electronics. Explore the article to understand which ink suits your specific printing needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
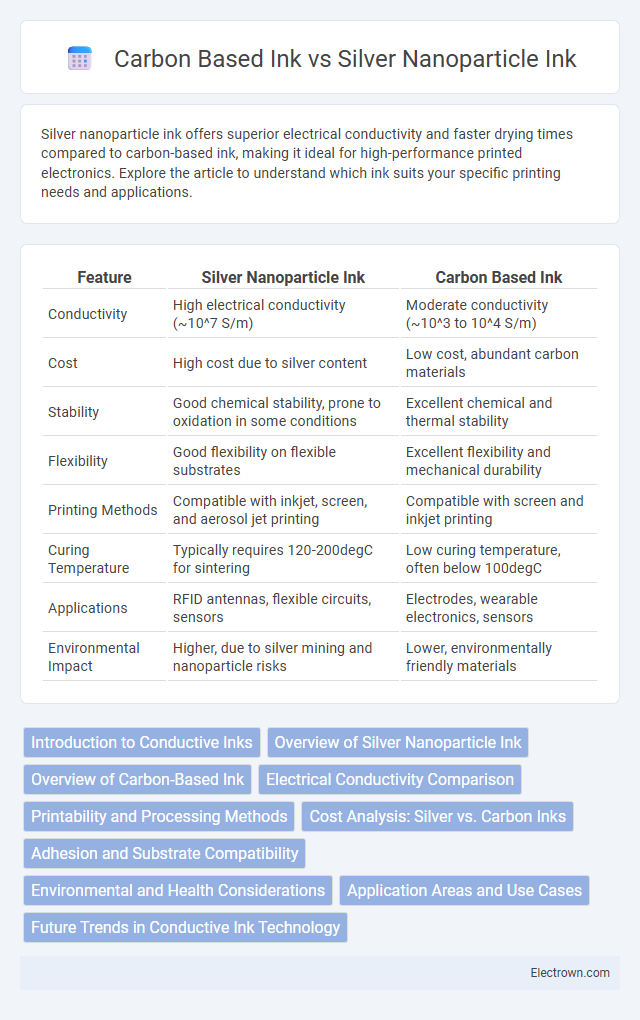
| Feature | Silver Nanoparticle Ink | Carbon Based Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity (~10^7 S/m) | Moderate conductivity (~10^3 to 10^4 S/m) |
| Cost | High cost due to silver content | Low cost, abundant carbon materials |
| Stability | Good chemical stability, prone to oxidation in some conditions | Excellent chemical and thermal stability |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility on flexible substrates | Excellent flexibility and mechanical durability |
| Printing Methods | Compatible with inkjet, screen, and aerosol jet printing | Compatible with screen and inkjet printing |
| Curing Temperature | Typically requires 120-200degC for sintering | Low curing temperature, often below 100degC |
| Applications | RFID antennas, flexible circuits, sensors | Electrodes, wearable electronics, sensors |
| Environmental Impact | Higher, due to silver mining and nanoparticle risks | Lower, environmentally friendly materials |
Introduction to Conductive Inks
Silver nanoparticle ink offers superior electrical conductivity and reliability, making it ideal for high-performance flexible electronics and printed circuit applications. Carbon-based ink provides cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives with moderate conductivity, preferred for sensors and low-power devices. Your choice depends on balancing conductivity needs, cost, and application-specific performance requirements.
Overview of Silver Nanoparticle Ink
Silver nanoparticle ink consists of conductive silver particles suspended in a liquid medium, offering superior electrical conductivity and high stability in printed electronics. This ink enables precise, low-resistance circuit patterns ideal for flexible electronics, RFID tags, and sensors, outperforming carbon-based inks which generally have higher resistivity. Your choice of silver nanoparticle ink ensures enhanced performance for applications demanding reliable conductivity and fine feature resolution.
Overview of Carbon-Based Ink
Carbon-based ink utilizes conductive carbon materials such as graphite, graphene, or carbon nanotubes, offering excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility for printed electronics. It provides cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to silver nanoparticle ink, with superior chemical stability and resistance to oxidation. Your printed circuits benefit from carbon-based ink's ability to maintain performance under harsh conditions and flexible substrates.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Silver nanoparticle ink offers significantly higher electrical conductivity compared to carbon-based ink, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications. Its conductivity typically ranges between 10^4 to 10^6 S/cm, whereas carbon-based inks often exhibit much lower values around 10^2 to 10^3 S/cm. If your project demands superior signal transmission and minimal resistive losses, silver nanoparticle ink is the preferable choice.
Printability and Processing Methods
Silver nanoparticle ink offers superior printability due to its excellent electrical conductivity and compatibility with diverse printing techniques like inkjet and screen printing, enabling fine pattern resolution and rapid curing. Carbon-based ink, while more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, may require higher sintering temperatures or additional processing steps to achieve comparable conductivity and adhesion on flexible substrates. Your choice depends on the balance between processing complexity, substrate compatibility, and desired electrical performance for your printed electronics application.
Cost Analysis: Silver vs. Carbon Inks
Silver nanoparticle ink commands a higher cost due to the precious metal content and complex synthesis process, which impacts overall production expenses. Carbon-based inks are significantly more affordable, derived from abundant raw materials like graphite or carbon black, making them cost-effective for large-scale printing applications. Your choice between silver and carbon inks should consider both initial material costs and the conductivity requirements of the final product.
Adhesion and Substrate Compatibility
Silver nanoparticle ink exhibits excellent adhesion on a wide range of substrates, including flexible plastics, glass, and textiles, due to its strong metallic bonding properties. Carbon-based ink, while offering good compatibility with porous substrates like paper and textiles, often requires surface treatments to achieve comparable adhesion levels on smooth or non-porous materials. Optimizing your choice based on substrate type ensures better durability and performance in printed electronics or sensor applications.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Silver nanoparticle ink poses significant environmental concerns due to its potential toxicity and bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems, raising risks for aquatic life and human health through water contamination. Carbon-based ink offers a safer alternative with lower environmental impact, as its organic composition reduces toxicity and improves biodegradability, making it more eco-friendly for printing applications. Your choice of ink should factor in these health and environmental considerations to minimize ecological damage and ensure safer handling.
Application Areas and Use Cases
Silver nanoparticle ink is extensively used in printed electronics, including flexible circuits, RFID tags, and wearable sensors due to its excellent electrical conductivity and reliability. Carbon-based ink finds its applications in biosensors, supercapacitors, and energy storage devices, offering advantages like low cost, biocompatibility, and environmental sustainability. Your choice between these inks depends on specific use cases, balancing conductivity needs with cost efficiency and environmental considerations.
Future Trends in Conductive Ink Technology
Silver nanoparticle ink continues to dominate conductive ink technology due to its superior electrical conductivity and reliability in flexible electronics. Carbon-based inks are gaining traction for their cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and improved mechanical flexibility, making them ideal for wearable devices and large-area sensors. Your choice between these inks will depend on balancing performance requirements with emerging trends favoring eco-friendly, printable electronics.
Silver nanoparticle ink vs Carbon based ink Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com