MCPCB (Metal Core Printed Circuit Board) offers superior heat dissipation ideal for high-power applications, while FR4 PCB, made from fiberglass epoxy, is preferred for its affordability and versatility in standard electronics. Discover how choosing the right PCB impacts your project's performance by exploring the detailed comparison in the full article.
Table of Comparison
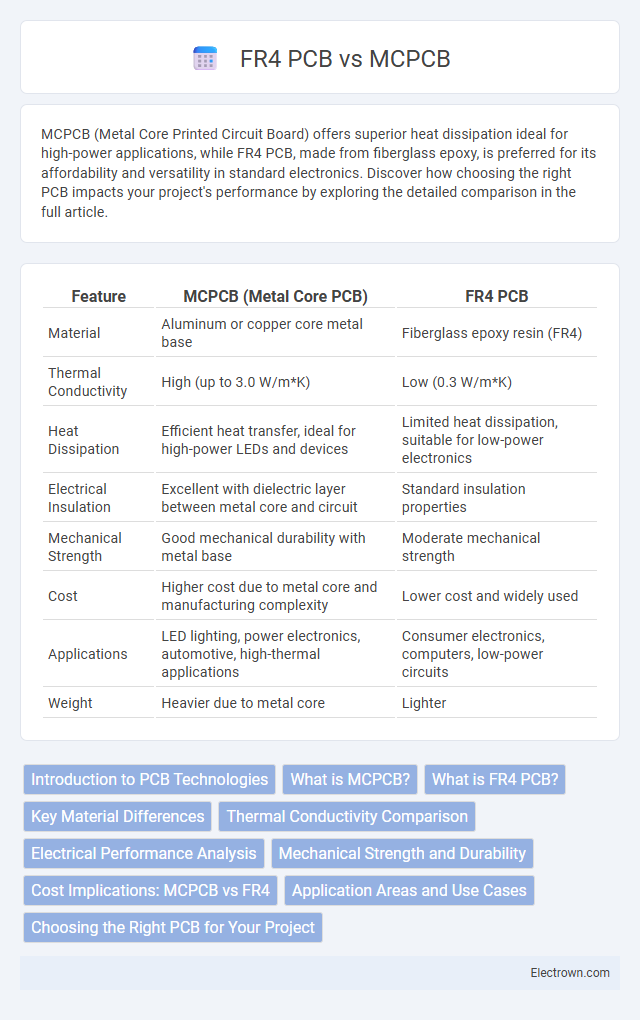
| Feature | MCPCB (Metal Core PCB) | FR4 PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum or copper core metal base | Fiberglass epoxy resin (FR4) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (up to 3.0 W/m*K) | Low (0.3 W/m*K) |
| Heat Dissipation | Efficient heat transfer, ideal for high-power LEDs and devices | Limited heat dissipation, suitable for low-power electronics |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent with dielectric layer between metal core and circuit | Standard insulation properties |
| Mechanical Strength | Good mechanical durability with metal base | Moderate mechanical strength |
| Cost | Higher cost due to metal core and manufacturing complexity | Lower cost and widely used |
| Applications | LED lighting, power electronics, automotive, high-thermal applications | Consumer electronics, computers, low-power circuits |
| Weight | Heavier due to metal core | Lighter |
Introduction to PCB Technologies
MCPCB (Metal Core Printed Circuit Board) features a metal base, typically aluminum, offering superior heat dissipation compared to FR4 PCB, which uses a fiberglass epoxy resin substrate. You benefit from MCPCB in high-power applications requiring efficient thermal management, while FR4 is suitable for general-purpose electronics with lower heat demands. These distinct materials impact durability, thermal conductivity, and cost, influencing your choice based on the specific device requirements.
What is MCPCB?
MCPCB, or Metal Core Printed Circuit Board, features a metal base such as aluminum or copper to enhance heat dissipation, making it ideal for high-power applications like LED lighting and power electronics. Compared to traditional FR4 PCB, which uses a fiberglass epoxy substrate, MCPCB provides superior thermal management and mechanical stability. Understanding your needs for heat conduction and durability will help determine whether MCPCB or FR4 PCB is the better choice for your project.
What is FR4 PCB?
FR4 PCB is a widely used type of printed circuit board made from woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder, offering excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength. It provides a sturdy, cost-effective solution for a broad range of electronic applications, but has lower thermal conductivity compared to MCPCB, making it less ideal for high-heat environments. Your choice of FR4 PCB suits projects where durability and electrical performance are important, but advanced heat dissipation is not critical.
Key Material Differences
MCPCB (Metal Core Printed Circuit Board) features a metal layer, typically aluminum or copper, providing superior thermal conductivity compared to the FR4 PCB, which uses a fiberglass epoxy resin as its base material. The metal core in MCPCBs efficiently dissipates heat generated by high-power components, making it ideal for LED lighting and power electronics, while FR4's insulated substrate offers excellent electrical performance but lower heat dissipation. Your choice depends on thermal management needs, with MCPCBs excelling in heat-sensitive applications and FR4 PCBs suited for standard electronic devices.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
MCPCBs (Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards) exhibit significantly higher thermal conductivity compared to FR4 PCBs due to their metal core, typically aluminum or copper, which efficiently dissipates heat. While FR4 PCBs have a thermal conductivity around 0.3-0.4 W/mK, MCPCBs can achieve thermal conductivity values exceeding 1.0 W/mK, making them ideal for high-power LED applications and power electronics. Enhanced heat dissipation in MCPCBs reduces thermal stress on components, improving reliability and performance in demanding environments.
Electrical Performance Analysis
MCPCB offers superior electrical performance compared to FR4 PCB due to its enhanced thermal conductivity, which effectively dissipates heat and reduces electrical resistance in high-power applications. The metal core in MCPCBs minimizes signal loss and maintains stable impedance, improving overall circuit reliability and efficiency. FR4 PCBs exhibit higher dielectric loss and limited heat dissipation, making them less efficient for high-frequency and high-current electronic devices.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
MCPCBs (Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards) offer superior mechanical strength and durability compared to FR4 PCBs due to their metal core, which provides enhanced resistance to bending, impact, and thermal stress. The metal core in MCPCBs dissipates heat more effectively, reducing the risk of warping and extending the lifespan of the board in high-power applications. FR4 PCBs, made of fiberglass epoxy resin, are generally less robust and more prone to mechanical damage under heavy loads or extreme environmental conditions.
Cost Implications: MCPCB vs FR4
MCPCBs generally have higher upfront costs compared to FR4 PCBs due to their specialized metal core designed for superior heat dissipation in high-power applications. FR4 PCBs are more cost-effective for standard electronic devices, offering lower material and manufacturing expenses suited to lower thermal requirements. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for efficient thermal management in your project.
Application Areas and Use Cases
MCPCB (Metal Core Printed Circuit Board) excels in high-power LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power converters due to its superior heat dissipation capabilities. FR4 PCB, commonly used in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and computer hardware, offers cost-effective insulation and mechanical stability for low to moderate thermal demands. Your choice should align with the thermal management requirements and application environment for optimal performance.
Choosing the Right PCB for Your Project
MCPCB offers superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for LED lighting and high-power applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. FR4 PCB, with its excellent electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness, suits general electronics with moderate thermal demands. Your project's performance and reliability will depend on selecting MCPCB for heat-sensitive designs or FR4 for standard circuit requirements.
MCPCB vs FR4 PCB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com