SOIC packages offer a more compact, surface-mount design ideal for high-density circuit boards, while DIP packages provide through-hole mounting, which is easier for manual soldering and prototyping. Explore the rest of the article to understand which package best suits your electronic project needs and design constraints.
Table of Comparison
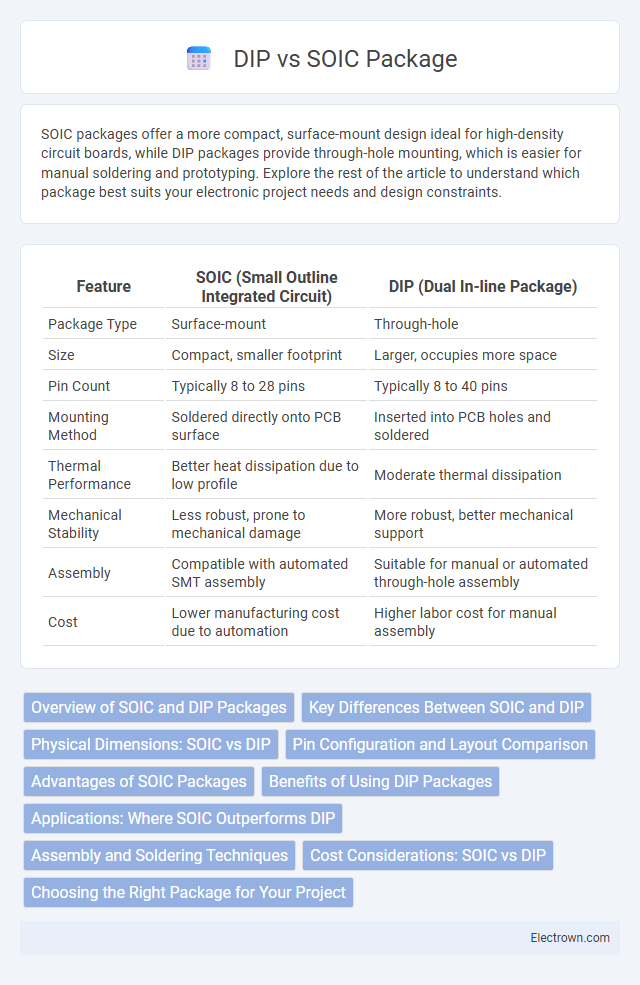
| Feature | SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) | DIP (Dual In-line Package) |
|---|---|---|
| Package Type | Surface-mount | Through-hole |
| Size | Compact, smaller footprint | Larger, occupies more space |
| Pin Count | Typically 8 to 28 pins | Typically 8 to 40 pins |
| Mounting Method | Soldered directly onto PCB surface | Inserted into PCB holes and soldered |
| Thermal Performance | Better heat dissipation due to low profile | Moderate thermal dissipation |
| Mechanical Stability | Less robust, prone to mechanical damage | More robust, better mechanical support |
| Assembly | Compatible with automated SMT assembly | Suitable for manual or automated through-hole assembly |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost due to automation | Higher labor cost for manual assembly |
Overview of SOIC and DIP Packages
SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) and DIP (Dual In-line Package) are common IC packaging types used in electronic devices. SOIC features a compact, surface-mount design with gull-wing leads suitable for automated assembly, while DIP has through-hole leads designed for easy manual insertion on PCB boards. Understanding these packages helps optimize Your circuit design by balancing space, assembly method, and reliability requirements.
Key Differences Between SOIC and DIP
SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) and DIP (Dual In-line Package) differ significantly in size and pin configuration, with SOIC offering a more compact footprint ideal for high-density PCB layouts, while DIP features a larger, through-hole design suited for prototyping and manual soldering. Thermal performance also varies, as DIP packages typically dissipate heat better due to their larger lead frames. Understanding these key differences helps optimize Your circuit design for space constraints, manufacturing processes, and thermal management needs.
Physical Dimensions: SOIC vs DIP
The SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) package typically measures about 3.9mm to 10.3mm in width with a low profile height around 1.75mm, offering a more compact form factor compared to the DIP (Dual In-line Package). DIP packages usually range from 7.62mm to over 15mm in width with a taller body height around 3.3mm to 5.1mm, resulting in a bulkier footprint suitable for through-hole mounting. These dimensional differences influence PCB layout design, with SOIC favoring high-density surface mount applications and DIP fitting simpler prototyping or legacy systems.
Pin Configuration and Layout Comparison
SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) packages feature a gull-wing lead design with pins extending from the sides, typically arranged in a single row per side, allowing for a more compact and space-efficient layout compared to the DIP (Dual In-line Package). DIP packages have pins protruding perpendicularly from two parallel rows, making them easier to handle and insert into through-hole PCB layouts but occupying more board space. The pin pitch in SOIC is generally smaller, around 1.27 mm, compared to DIP's larger standard pitch of 2.54 mm, which influences soldering techniques and PCB routing complexity.
Advantages of SOIC Packages
SOIC packages offer significant advantages such as smaller footprint and lower profile compared to DIP packages, enabling higher-density circuit designs and improved performance in compact electronic devices. The thin, surface-mount format reduces lead inductance and resistance, enhancing signal integrity and thermal dissipation. SOIC packages also facilitate automated PCB assembly processes, increasing manufacturing efficiency and reliability.
Benefits of Using DIP Packages
DIP packages offer superior ease of prototyping and manual soldering due to their through-hole design, which provides stronger mechanical bonds on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Their larger size facilitates better heat dissipation, enhancing reliability in high-power applications. DIP packages also simplify testing and replacement in circuitry, making them ideal for educational and development purposes.
Applications: Where SOIC Outperforms DIP
SOIC packages outperform DIP packages in applications requiring high-density circuit designs, such as modern consumer electronics and compact medical devices, due to their smaller footprint and lower profile. SOIC's surface-mount technology enables automated assembly processes, increasing manufacturing efficiency in complex PCBs for smartphones and laptops. Their superior thermal performance and reduced parasitic inductance make SOIC ideal for high-frequency and high-speed signal processing applications.
Assembly and Soldering Techniques
SOIC packages feature gull-wing leads that facilitate automated surface-mount assembly and reflow soldering, providing precise placement and minimal lead damage. DIP packages are designed for through-hole assembly, requiring hand soldering or wave soldering, which may be slower but offers strong mechanical connections suitable for prototyping. Your choice between SOIC and DIP affects soldering efficiency, assembly speed, and the suitability for automated or manual processes.
Cost Considerations: SOIC vs DIP
SOIC packages typically offer lower manufacturing and assembly costs compared to DIP due to their smaller size and compatibility with automated surface-mount technology (SMT), reducing labor expenses. DIP packages, while generally more expensive per unit, provide easier manual handling and prototyping flexibility, which can save costs in low-volume or repair scenarios. Your choice between SOIC and DIP should factor in production volume and assembly methods to optimize overall cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Package for Your Project
Choosing between SOIC and DIP packages depends on project requirements such as space constraints, ease of soldering, and circuit complexity. SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) offers a compact surface-mount solution ideal for high-density PCBs, while DIP (Dual In-line Package) provides through-hole mounting that simplifies prototyping and manual assembly. Consider factors like PCB layout, automated production capabilities, and thermal management when selecting the appropriate IC package.
SOIC vs DIP package Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com