Silver paste offers superior electrical conductivity and durability compared to carbon paste, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications. Discover which paste best suits your needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
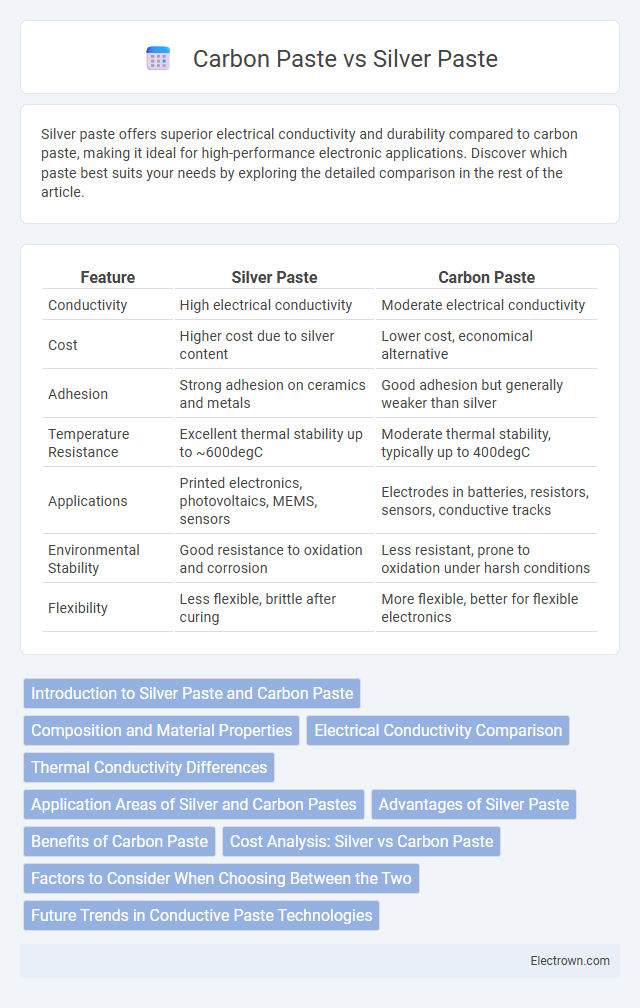
| Feature | Silver Paste | Carbon Paste |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity | Moderate electrical conductivity |
| Cost | Higher cost due to silver content | Lower cost, economical alternative |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion on ceramics and metals | Good adhesion but generally weaker than silver |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent thermal stability up to ~600degC | Moderate thermal stability, typically up to 400degC |
| Applications | Printed electronics, photovoltaics, MEMS, sensors | Electrodes in batteries, resistors, sensors, conductive tracks |
| Environmental Stability | Good resistance to oxidation and corrosion | Less resistant, prone to oxidation under harsh conditions |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, brittle after curing | More flexible, better for flexible electronics |
Introduction to Silver Paste and Carbon Paste
Silver paste consists of fine silver particles suspended in a binder, offering excellent electrical conductivity and durability for electronic applications such as solar cells and printed circuit boards. Carbon paste, made from carbon particles mixed with a binder, provides good conductivity with cost-effectiveness and chemical stability, commonly used in sensors and resistors. Your choice between silver and carbon paste depends on the required conductivity, cost constraints, and specific application needs.
Composition and Material Properties
Silver paste comprises micron-sized silver particles suspended in an organic binder, offering excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability. Carbon paste contains carbon black or graphite particles within a polymer matrix, providing moderate conductivity and greater chemical resistance. Your choice depends on the need for high conductivity with silver paste or cost-effective, corrosion-resistant properties with carbon paste.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Silver paste exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than carbon paste due to silver's superior metallic properties, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications requiring minimal resistance. Carbon paste offers adequate conductivity for lower-cost, less critical circuits but falls short in efficiency compared to silver paste. If your project demands optimal current flow and signal integrity, silver paste is the preferred choice for reliable performance.
Thermal Conductivity Differences
Silver paste exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity, typically around 300 W/m*K, compared to carbon paste, which usually ranges between 5-10 W/m*K. This makes silver paste highly effective for applications requiring rapid heat dissipation, such as in electronics cooling and thermal interface materials. Carbon paste, with its lower thermal conductivity, is more suited for applications where electrical conductivity and cost efficiency are prioritized over thermal management.
Application Areas of Silver and Carbon Pastes
Silver paste is widely used in photovoltaic cells, printed electronics, and conductive adhesives due to its superior electrical conductivity and stability under high temperatures. Carbon paste is commonly applied in sensors, batteries, and electrochemical electrodes, prized for its chemical inertness and cost-effectiveness. Both materials serve critical roles in electronic devices, with silver paste favored for high-performance circuits and carbon paste preferred in applications where budget and chemical resistance are essential.
Advantages of Silver Paste
Silver paste offers superior electrical conductivity and enhanced durability compared to carbon paste, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications. Its excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidation ensure reliable long-term operation in harsh environments. These advantages contribute to improved efficiency and lifespan in printed circuit boards and photovoltaic cells.
Benefits of Carbon Paste
Carbon paste offers superior conductivity and flexibility compared to silver paste, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and lightweight materials. It is more cost-effective due to the lower price of carbon compared to silver, providing an economical solution for large-scale electronic manufacturing. Additionally, carbon paste demonstrates excellent resistance to oxidation and thermal stability, enhancing the longevity and reliability of printed electronic circuits.
Cost Analysis: Silver vs Carbon Paste
Silver paste commands a higher price due to its excellent electrical conductivity and superior durability, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications. Carbon paste offers a cost-effective alternative with adequate conductivity for less demanding uses, significantly reducing material expenses. Your choice between silver and carbon paste should balance budget constraints with the required electrical performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between the Two
When choosing between silver paste and carbon paste, factors such as electrical conductivity, cost, and application requirements are crucial. Silver paste offers superior conductivity and durability, making it ideal for high-performance electronic circuits, while carbon paste is more cost-effective and suitable for low-power applications. Your decision should also consider environmental stability, adhesion properties, and the specific substrate compatibility to ensure optimal performance in your project.
Future Trends in Conductive Paste Technologies
Future trends in conductive paste technologies emphasize the development of eco-friendly, high-performance silver pastes with enhanced conductivity and thermal stability for advanced electronics. Carbon pastes are evolving with improved conductivity and flexibility, targeting applications in wearable devices and flexible circuits. Both materials are increasingly integrated with nanomaterials and 3D printing techniques to optimize performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Silver paste vs Carbon paste Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com