Surface Mount Technology (SMT) offers faster production and smaller component sizes compared to Through-Hole Technology (THD), which provides stronger mechanical bonds ideal for high-stress applications. Explore the article to understand which technology suits Your specific electronic manufacturing needs.
Table of Comparison
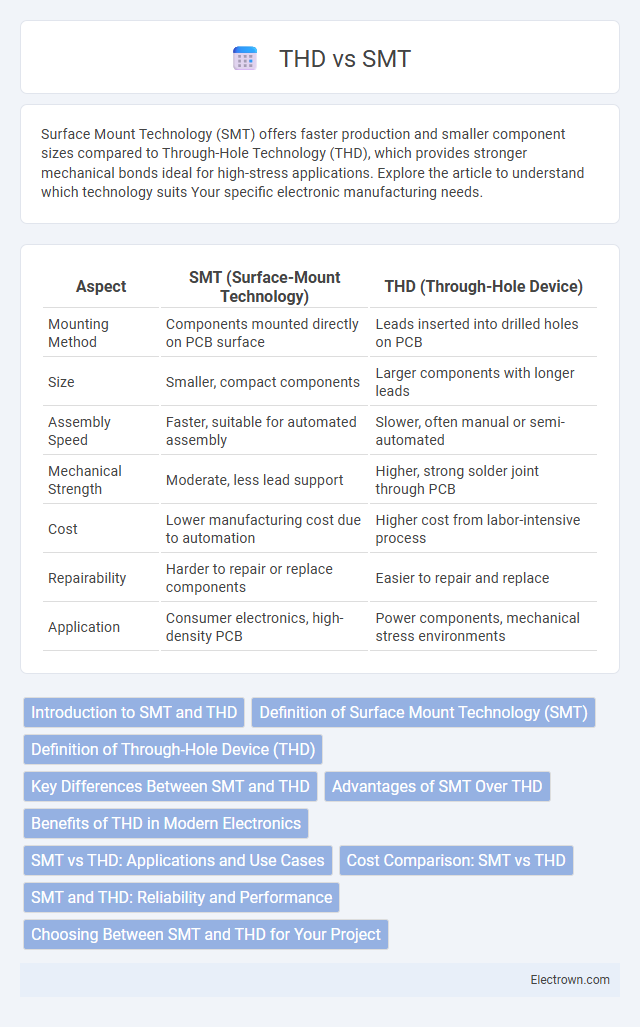
| Aspect | SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) | THD (Through-Hole Device) |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting Method | Components mounted directly on PCB surface | Leads inserted into drilled holes on PCB |
| Size | Smaller, compact components | Larger components with longer leads |
| Assembly Speed | Faster, suitable for automated assembly | Slower, often manual or semi-automated |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, less lead support | Higher, strong solder joint through PCB |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost due to automation | Higher cost from labor-intensive process |
| Repairability | Harder to repair or replace components | Easier to repair and replace |
| Application | Consumer electronics, high-density PCB | Power components, mechanical stress environments |
Introduction to SMT and THD
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Device (THD) are two primary methods used for mounting electronic components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). SMT involves placing components directly onto the board's surface, enabling higher component density and automated assembly processes. THD requires inserting component leads through drilled holes on the PCB and soldering them on the opposite side, offering stronger mechanical bonds ideal for heavy or high-stress applications.
Definition of Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method for producing electronic circuits where components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), enabling compact designs and enhanced electrical performance. This technology contrasts with Through-Hole Device (THD) technology, which involves inserting leads into drilled holes on the PCB. Your choice between SMT and THD impacts manufacturing efficiency, component density, and overall product reliability.
Definition of Through-Hole Device (THD)
Through-Hole Device (THD) refers to electronic components with leads inserted into drilled holes on a printed circuit board (PCB) and soldered on the opposite side, ensuring robust mechanical strength. This mounting technique, widely used before Surface-Mount Technology (SMT), accommodates larger and high-power components such as transformers and connectors. THD provides superior durability and is preferred in applications requiring strong physical connections and enhanced heat dissipation.
Key Differences Between SMT and THD
SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) and THD (Through-Hole Devices) differ primarily in component mounting techniques; SMT components are mounted directly onto the PCB surface, enabling higher circuit density and smaller board size, while THD components use leads inserted through holes on the PCB for soldering. SMT offers faster assembly, better performance at high frequencies, and cost efficiency in mass production, whereas THD provides stronger mechanical bonds and is preferred for components subject to mechanical stress. The choice between SMT and THD impacts design complexity, manufacturing costs, and repairability of electronic assemblies.
Advantages of SMT Over THD
Surface-mount technology (SMT) offers significant advantages over through-hole technology (THD), including smaller component size and higher circuit density for advanced electronic designs. SMT enables automated assembly processes, leading to faster production speeds and reduced manufacturing costs. Your electronics designs benefit from improved electrical performance and greater reliability due to minimized lead inductance and better heat dissipation with SMT components.
Benefits of THD in Modern Electronics
THD (Through-Hole Device) technology offers superior mechanical strength and reliable electrical connections, making it ideal for high-stress environments in modern electronics. It provides better heat dissipation and durability compared to SMT (Surface Mount Technology), ensuring longer device lifespan and performance stability. Your electronic designs benefit from enhanced robustness and ease of prototyping when utilizing THD components.
SMT vs THD: Applications and Use Cases
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) excels in compact, high-density electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and automotive control systems due to its efficient use of PCB space and automated assembly. THD (Through-Hole Technology) remains preferred for applications requiring robust mechanical bonds and higher durability, like industrial machinery, aerospace equipment, and power supplies. Understanding these distinct use cases helps optimize your design choices for performance, reliability, and manufacturing efficiency.
Cost Comparison: SMT vs THD
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) generally offers lower production costs due to automated assembly processes and reduced material usage compared to Through-Hole Technology (THD). THD incurs higher expenses from manual labor, longer production times, and increased use of components, making it less cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing. SMT's cost efficiency enhances scalability and is favored in industries prioritizing rapid, economical production.
SMT and THD: Reliability and Performance
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) offers improved reliability and performance over Through-Hole Technology (THD) by enabling smaller component sizes and shorter electrical paths, resulting in reduced signal inductance and enhanced high-frequency performance. SMT components generally exhibit better resistance to vibration and mechanical stress due to their low-profile mounting, whereas THD provides superior mechanical strength for components exposed to physical strain. The choice between SMT and THD hinges on specific application requirements, including thermal management, electrical performance, and environmental durability.
Choosing Between SMT and THD for Your Project
Selecting between SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) and THD (Through-Hole Design) depends on your project's requirements for size, durability, and manufacturing complexity. SMT components offer compactness and automated assembly advantages, ideal for high-volume production and miniaturized devices, while THD provides stronger mechanical bonds suited for prototypes or products exposed to physical stress. Understanding these differences ensures you choose the most efficient and reliable technology tailored to your project's performance and cost objectives.
SMT vs THD Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com