Gold plating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance electronic connectors, while tin plating provides a cost-effective solution with good solderability and protection against oxidation. Explore the rest of the article to understand which plating suits your specific application requirements.
Table of Comparison
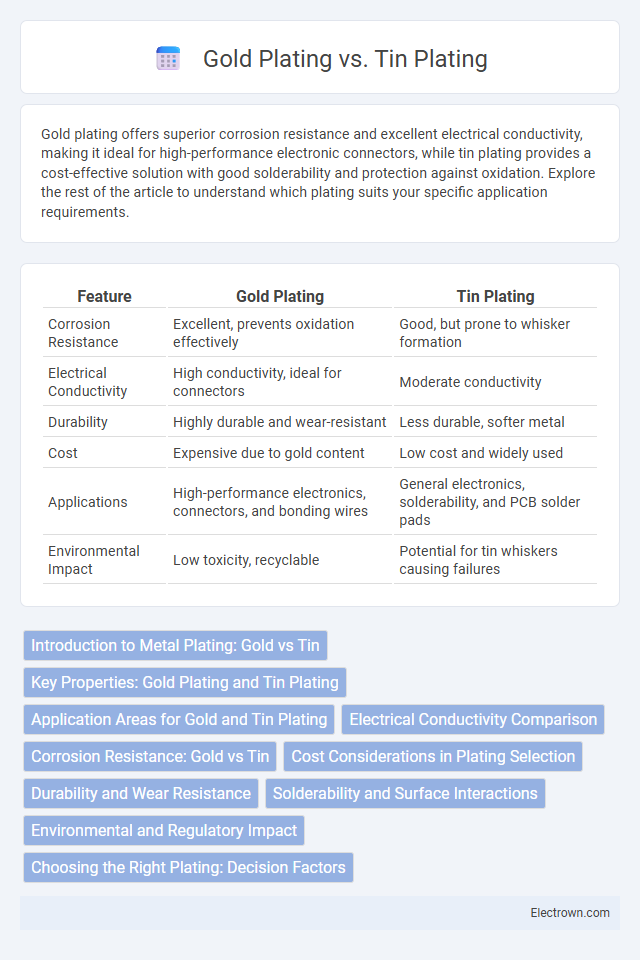
| Feature | Gold Plating | Tin Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, prevents oxidation effectively | Good, but prone to whisker formation |
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, ideal for connectors | Moderate conductivity |
| Durability | Highly durable and wear-resistant | Less durable, softer metal |
| Cost | Expensive due to gold content | Low cost and widely used |
| Applications | High-performance electronics, connectors, and bonding wires | General electronics, solderability, and PCB solder pads |
| Environmental Impact | Low toxicity, recyclable | Potential for tin whiskers causing failures |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Gold vs Tin
Gold plating offers superior corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and a highly attractive finish, making it ideal for high-performance electronics and luxury decorative applications. Tin plating provides excellent solderability, cost-effectiveness, and good corrosion resistance, commonly used in electrical connectors and food-grade packaging. Both plating methods enhance substrate durability and performance, with choice driven by specific environmental and functional requirements.
Key Properties: Gold Plating and Tin Plating
Gold plating offers exceptional corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and superior solderability, making it ideal for high-reliability electronic components. Tin plating provides good corrosion protection, cost-effectiveness, and easy solderability, but has lower conductivity and may form whiskers that affect long-term performance. The choice between gold and tin plating depends on application requirements such as durability, electrical performance, and budget constraints.
Application Areas for Gold and Tin Plating
Gold plating is extensively used in high-reliability electronic connectors, aerospace components, and medical devices due to its excellent corrosion resistance and superior electrical conductivity. Tin plating is commonly applied in printed circuit boards, automotive parts, and consumer electronics for cost-effective protection against oxidation and solderability. Both plating methods serve critical roles in enhancing the durability and performance of various industrial and commercial products.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Gold plating offers superior electrical conductivity compared to tin plating, with gold exhibiting a conductivity of approximately 45.2 million Siemens per meter (MS/m), whereas tin's conductivity is significantly lower at around 9.17 MS/m. This higher conductivity of gold reduces contact resistance, making it ideal for high-frequency and sensitive electronic applications. Tin plating, while less conductive, provides cost-effective corrosion resistance but may introduce higher resistance and potential signal loss in critical electrical contacts.
Corrosion Resistance: Gold vs Tin
Gold plating offers superior corrosion resistance due to its inert nature and excellent ability to prevent oxidation, making it ideal for high-reliability electronic components. Tin plating, while more cost-effective, is prone to oxidation and whisker growth, which can compromise long-term corrosion protection and electrical performance. Choosing gold over tin plating significantly enhances durability in harsh environments where corrosion resistance is critical.
Cost Considerations in Plating Selection
Gold plating offers superior corrosion resistance and conductivity but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to tin plating, making tin a more budget-friendly option for large-scale or cost-sensitive applications. Tin plating provides effective protection against oxidation and is widely used for its affordability and reliability in standard environments. When selecting plating, your decision should balance performance requirements against cost constraints to ensure optimal value for your application.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Gold plating offers superior durability and wear resistance due to its corrosion resistance and non-oxidizing properties, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical connections. Tin plating provides good conductivity and solderability but is more prone to wear and oxidation over time, reducing its lifespan in harsh environments. For applications requiring longevity and consistent performance, you should consider gold plating to ensure better protection against wear and environmental factors.
Solderability and Surface Interactions
Gold plating offers superior solderability due to its corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, ensuring reliable surface interactions during assembly. Tin plating provides good solderability as well, but is more prone to oxidation, which can affect surface wetting and long-term durability. Your choice between gold and tin plating depends on the specific requirements for solder joint quality and environmental factors in your application.
Environmental and Regulatory Impact
Gold plating offers superior corrosion resistance and durability but involves more complex mining and refining processes, raising environmental concerns related to heavy metal extraction and waste management. Tin plating presents a more eco-friendly alternative with lower toxicity and simpler recycling, aligning better with regulations such as RoHS that limit hazardous substances in electronics. Choosing between the two affects Your compliance with environmental standards and sustainability goals in manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Plating: Decision Factors
Gold plating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electronic components and connectors. Tin plating provides cost-effective corrosion protection and good solderability, suitable for general-purpose applications where budget constraints are important. Key decision factors include environmental exposure, required conductivity, mechanical durability, and budget considerations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
gold plating vs tin plating Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com