Flip chip technology offers superior electrical performance and higher density connections compared to wire bonding by allowing direct chip-to-substrate contact, reducing signal loss and inductance. Explore the rest of the article to understand which packaging method best suits your semiconductor needs.
Table of Comparison
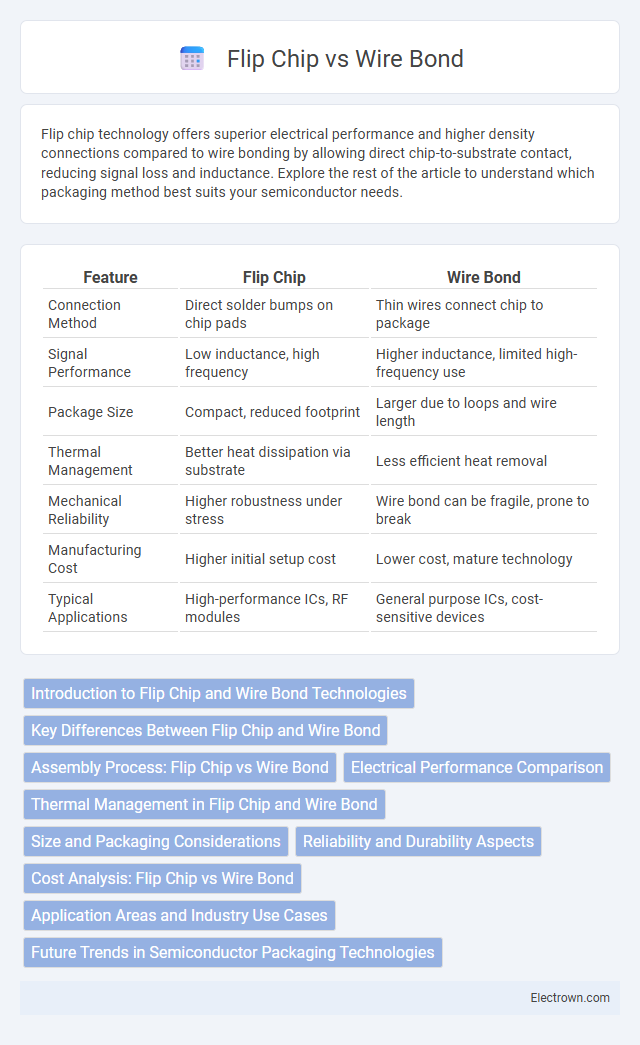
| Feature | Flip Chip | Wire Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Method | Direct solder bumps on chip pads | Thin wires connect chip to package |
| Signal Performance | Low inductance, high frequency | Higher inductance, limited high-frequency use |
| Package Size | Compact, reduced footprint | Larger due to loops and wire length |
| Thermal Management | Better heat dissipation via substrate | Less efficient heat removal |
| Mechanical Reliability | Higher robustness under stress | Wire bond can be fragile, prone to break |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher initial setup cost | Lower cost, mature technology |
| Typical Applications | High-performance ICs, RF modules | General purpose ICs, cost-sensitive devices |
Introduction to Flip Chip and Wire Bond Technologies
Flip chip technology involves directly attaching the semiconductor die to the substrate using solder bumps, enabling shorter electrical paths and improved performance for advanced integrated circuits. Wire bond technology connects the die to the package lead frame with fine metal wires, offering cost-effective and mature solutions for many semiconductor applications. Both techniques play critical roles in semiconductor packaging, with flip chip preferred for high-frequency and high-density designs while wire bonding remains widely used in standard and low-cost devices.
Key Differences Between Flip Chip and Wire Bond
Flip chip technology enables direct electrical connections through solder bumps on the chip's surface, providing shorter interconnects and improved performance compared to wire bond's wire loops. Wire bond uses fine wires to connect the chip to the package leads, which can introduce higher inductance and lower signal integrity. Your choice between flip chip and wire bond impacts device speed, reliability, and heat dissipation in semiconductor packaging.
Assembly Process: Flip Chip vs Wire Bond
The assembly process for flip chip involves directly mounting the semiconductor die face-down onto the substrate using solder bumps, enabling shorter electrical paths and improved performance. In contrast, wire bond assembly connects the die to the package via fine wires, which can introduce longer signal paths and potential inductance. Your choice between flip chip and wire bond impacts assembly complexity, thermal management, and overall device reliability.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Flip chip technology offers superior electrical performance compared to wire bonding due to its shorter interconnect paths and reduced parasitic inductance and capacitance. This results in faster signal transmission and lower resistance, which is critical for high-frequency and high-speed applications. Your designs can achieve enhanced signal integrity and improved power efficiency with flip chip packaging over traditional wire bond methods.
Thermal Management in Flip Chip and Wire Bond
Flip chip technology offers superior thermal management compared to wire bond due to its shorter thermal paths and direct die-to-substrate contact, enabling efficient heat dissipation. Wire bond packages rely on longer interconnects, which increase thermal resistance and limit heat flow away from the die. Enhanced thermal conductivity in flip chip assemblies improves device performance and reliability, particularly in high-power and high-frequency applications.
Size and Packaging Considerations
Flip chip technology offers a smaller package size compared to wire bond due to its direct die-to-substrate connection, reducing the overall footprint and enabling higher component density. Wire bond requires more space for bond pads and wire loops, which can lead to larger package dimensions and increased parasitic inductance. Your choice between flip chip and wire bond depends on the desired miniaturization and packaging constraints of your electronic design.
Reliability and Durability Aspects
Flip chip technology offers superior reliability and durability compared to wire bonding due to its shorter interconnects and robust solder bumps, which reduce signal inductance and resist mechanical stress better. Wire bond connections are more susceptible to damage from thermal cycling and mechanical fatigue because of their longer, fragile gold or aluminum wires. The enhanced thermal performance and mechanical stability of flip chip assemblies make them more suitable for high-frequency and high-reliability applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
Cost Analysis: Flip Chip vs Wire Bond
Flip chip technology generally has higher upfront costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and equipment, but offers lower per-unit costs at high volumes because of reduced packaging size and improved performance. Wire bond remains cost-effective for low to medium production volumes, with simpler assembly and lower initial investment. Your choice between flip chip and wire bond should consider production volume, performance requirements, and total cost of ownership.
Application Areas and Industry Use Cases
Flip chip technology excels in high-frequency applications such as RF modules, smartphones, and medical devices due to its superior electrical performance and reduced parasitic inductance. Wire bonding remains prevalent in automotive electronics, industrial sensors, and consumer products, offering cost-effective and reliable interconnections for medium to low-frequency circuits. Your choice between flip chip and wire bond depends on performance requirements and specific industry applications where factors like thermal management and miniaturization are critical.
Future Trends in Semiconductor Packaging Technologies
Future trends in semiconductor packaging technologies emphasize increasing adoption of flip chip over traditional wire bond due to its superior electrical performance, smaller footprint, and enhanced thermal management. Flip chip technology supports higher input/output density and better signal integrity, crucial for advanced applications like 5G, AI, and IoT devices. Your designs will benefit from improved reliability and miniaturization as the industry moves toward heterogeneous integration and advanced packaging solutions such as fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) and 3D stacking.
flip chip vs wire bond Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com