AC motors offer efficient power conversion and are widely used in industrial applications due to their durability and low maintenance, while DC motors provide precise speed control and high starting torque, making them ideal for specialized tasks. Explore the rest of the article to understand which motor best suits your specific needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
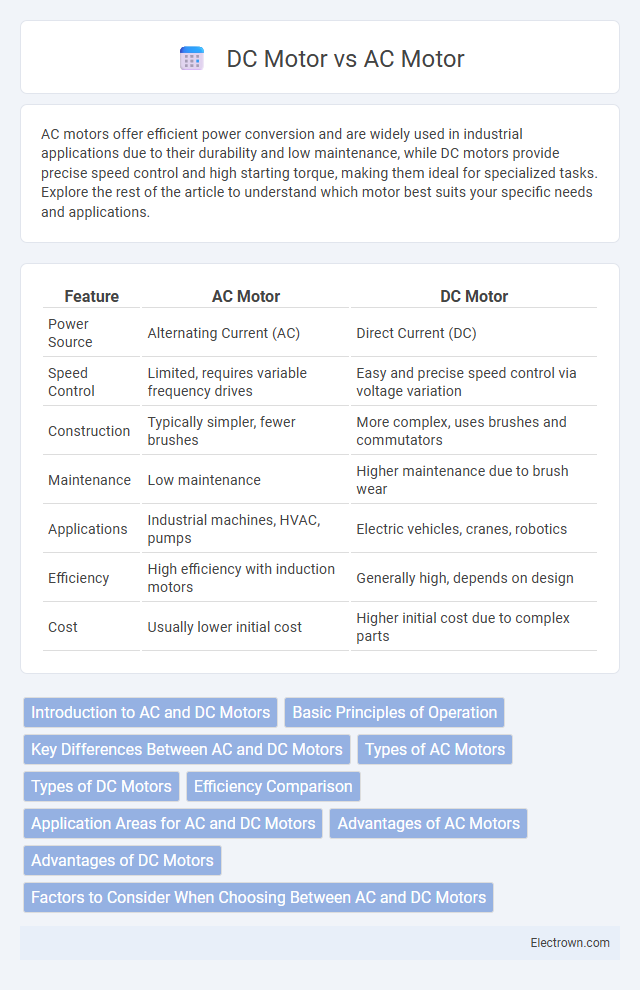
| Feature | AC Motor | DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Speed Control | Limited, requires variable frequency drives | Easy and precise speed control via voltage variation |
| Construction | Typically simpler, fewer brushes | More complex, uses brushes and commutators |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Higher maintenance due to brush wear |
| Applications | Industrial machines, HVAC, pumps | Electric vehicles, cranes, robotics |
| Efficiency | High efficiency with induction motors | Generally high, depends on design |
| Cost | Usually lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to complex parts |
Introduction to AC and DC Motors
AC motors operate using alternating current, which reverses direction periodically, enabling efficient power transmission in industrial and household applications. DC motors rely on direct current, providing constant voltage and allowing precise speed and torque control, commonly used in electric vehicles and robotics. Both motor types convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, but their distinct current sources influence performance characteristics and suitable use cases.
Basic Principles of Operation
AC motors operate by utilizing alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field that induces torque on the rotor, enabling continuous rotation. DC motors function by passing direct current through windings on the rotor, creating a magnetic field that interacts with the stator's magnetic field to generate motion. The fundamental difference lies in AC motors relying on electromagnetic induction with alternating current, whereas DC motors use a commutator system to maintain unidirectional current flow in the rotor windings.
Key Differences Between AC and DC Motors
AC motors operate on alternating current, providing efficient performance in applications with fluctuating load demands, while DC motors run on direct current, offering precise speed control and high starting torque. Key differences include AC motors' simpler construction and lower maintenance due to the absence of brushes, compared to the brush-equipped DC motors which require more upkeep. You should consider these factors based on your application's performance needs, control complexity, and maintenance requirements.
Types of AC Motors
AC motors include synchronous and induction motors, with induction motors further divided into single-phase and three-phase types, widely used in industrial and household applications due to their robustness and simple construction. Synchronous motors operate at constant speed, making them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control, while induction motors, especially squirrel-cage types, are popular for their efficiency and low maintenance. Understanding the specific types of AC motors helps you select the appropriate motor for your machinery or equipment needs, optimizing performance and energy consumption.
Types of DC Motors
DC motors are primarily classified into three types: brushed, brushless, and series-wound, each offering distinct operational characteristics suitable for various applications. Brushed DC motors use carbon brushes and a commutator for current switching, making them simple and cost-effective but with higher maintenance. Brushless DC motors utilize electronic commutation for improved efficiency and longevity, while series-wound DC motors provide high starting torque ideal for traction and heavy-duty equipment.
Efficiency Comparison
AC motors generally offer higher efficiency in fixed-speed applications due to lower power losses and simpler construction, making them ideal for large industrial systems. DC motors provide superior speed control and torque at varying loads but tend to have lower overall efficiency because of brush friction and commutator wear. Your choice depends on whether precise speed control or maximum energy efficiency is the priority in your application.
Application Areas for AC and DC Motors
AC motors are widely used in industrial applications such as fans, pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems where variable speed and high power output are required. DC motors excel in applications needing precise speed control and high starting torque, including electric vehicles, robotics, and small household appliances. The choice between AC and DC motors depends on factors like power source availability, control complexity, and performance requirements in sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, and consumer electronics.
Advantages of AC Motors
AC motors offer superior efficiency and require less maintenance due to their simpler construction without brushes or commutators. They are well-suited for applications requiring constant speed and can easily operate on standard power supply frequencies. High reliability and lower operational costs make AC motors ideal for industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and household appliances.
Advantages of DC Motors
DC motors offer precise speed control and high starting torque, making them ideal for applications requiring variable speed and load conditions. They provide consistent torque and efficient performance in low-speed operations, benefiting industrial machines and robotics. Their simple design allows easy maintenance and durability in demanding environments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between AC and DC Motors
When selecting between AC and DC motors, key factors include the application's speed control requirements, maintenance considerations, and power source availability. AC motors are typically preferred for consistent speed and low maintenance in industrial settings, while DC motors offer superior speed control and torque for precise applications. Your choice should align with performance needs, operational environment, and energy efficiency priorities.
AC Motor vs DC Motor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com