LED displays use light-emitting diodes as a backlight source, offering higher brightness and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCDs, which rely on cold cathode fluorescent lamps. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best screen technology for your needs, so continue reading to explore more about LED and LCD.
Table of Comparison
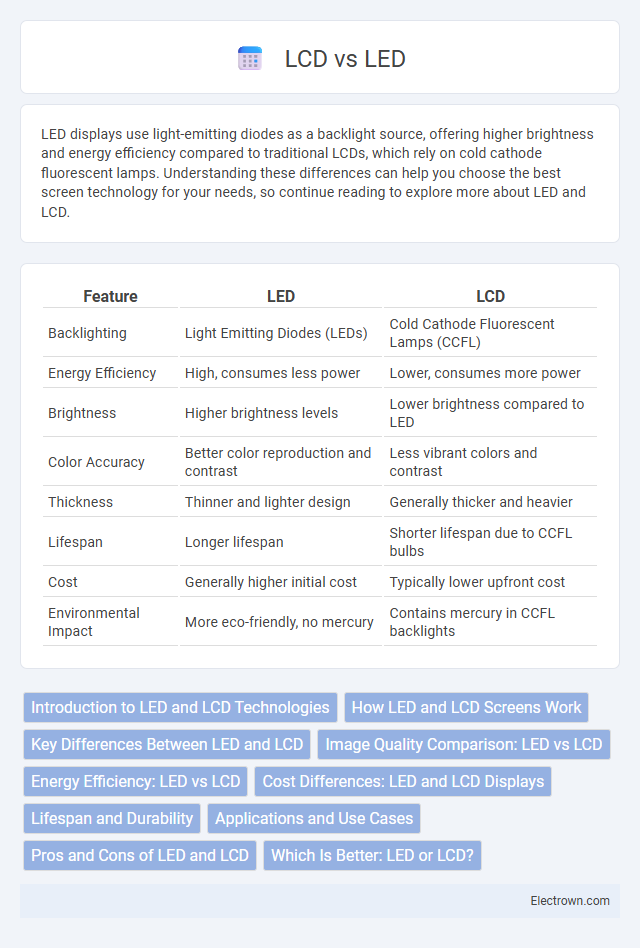
| Feature | LED | LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Backlighting | Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) | Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFL) |
| Energy Efficiency | High, consumes less power | Lower, consumes more power |
| Brightness | Higher brightness levels | Lower brightness compared to LED |
| Color Accuracy | Better color reproduction and contrast | Less vibrant colors and contrast |
| Thickness | Thinner and lighter design | Generally thicker and heavier |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan | Shorter lifespan due to CCFL bulbs |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Typically lower upfront cost |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly, no mercury | Contains mercury in CCFL backlights |
Introduction to LED and LCD Technologies
LED and LCD technologies both play critical roles in modern display screens, with LCDs using liquid crystal cells to modulate light and LEDs serving as the light source in many LCD panels or as self-emissive pixels in LED displays. LCD displays require a backlight, often provided by LEDs, which enhances brightness and energy efficiency compared to older CCFL backlights. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right screen technology based on factors like image quality, power consumption, and display thickness.
How LED and LCD Screens Work
LED screens use light-emitting diodes to create images by illuminating individual pixels, offering high brightness and energy efficiency. LCD screens rely on liquid crystal molecules modulating backlight to display visuals, which requires a separate light source. The primary difference lies in the light generation method, impacting contrast, color accuracy, and power consumption.
Key Differences Between LED and LCD
LED displays use light-emitting diodes as a backlight source, offering higher brightness and improved energy efficiency compared to LCDs, which rely on cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs). LCD screens control image quality through liquid crystal alignment but depend on external light sources, resulting in lower contrast ratios and less vibrant colors than LED technology. LED screens provide thinner designs, faster response times, and enhanced color accuracy, making them more suitable for modern high-definition applications.
Image Quality Comparison: LED vs LCD
LED displays generally offer superior image quality compared to traditional LCDs due to their ability to produce deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios by using individually lit LEDs. LCD screens rely on a backlight that can cause light bleed, reducing overall sharpness and color accuracy. Your viewing experience improves significantly with LED technology, providing more vivid colors, better brightness control, and enhanced detail in both dark and bright scenes.
Energy Efficiency: LED vs LCD
LED displays consume significantly less power than traditional LCDs due to their use of light-emitting diodes for backlighting, resulting in higher energy efficiency and longer battery life in portable devices. LCDs rely on cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) for illumination, which are less efficient and generate more heat. Energy-efficient LED technology reduces electricity costs and environmental impact, making it the preferred choice for modern screens.
Cost Differences: LED and LCD Displays
LED displays generally have higher upfront costs compared to traditional LCD screens due to advanced backlighting technology and enhanced energy efficiency. However, your long-term savings may increase with LED displays because they consume less power and have longer lifespans, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Understanding these cost differences helps you make an informed decision based on initial budget constraints versus total cost of ownership.
Lifespan and Durability
LED displays generally offer a longer lifespan and greater durability compared to LCD screens due to their use of organic or inorganic diodes that are less prone to burn-in and degradation. Your LED screen can typically last between 30,000 to 100,000 hours, whereas LCDs usually range from 20,000 to 60,000 hours before noticeable dimming or color shifts occur. The solid-state nature of LEDs also makes them more resistant to physical shocks and temperature fluctuations, enhancing overall durability in various environments.
Applications and Use Cases
LED displays excel in outdoor advertising, digital billboards, and large venue screens due to their high brightness, energy efficiency, and superior visibility in sunlight. LCDs are ideal for computer monitors, smartphones, and indoor TVs, offering precise color reproduction and sharp image quality in controlled lighting environments. Both technologies serve distinct needs: LEDs dominate in wide-area and high-impact displays, while LCDs are preferred for detailed, close-range viewing applications.
Pros and Cons of LED and LCD
LED displays offer higher contrast ratios, energy efficiency, and thinner designs compared to LCDs, making them ideal for vibrant visuals and modern aesthetics. LCD screens provide consistent color accuracy and are generally more affordable, but they tend to consume more power and have limited viewing angles. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy savings and image quality (LED) or budget and color consistency (LCD).
Which Is Better: LED or LCD?
LED displays use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, offering higher brightness, better contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD panels that rely on fluorescent backlighting. LCD screens excel in color accuracy and are generally more affordable, making them suitable for tasks requiring precise color representation. Choosing between LED and LCD depends on priorities such as image quality, power consumption, and budget constraints.
led vs lcd Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com