Polyimide offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polyester, making it ideal for high-performance engineering applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how each material suits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
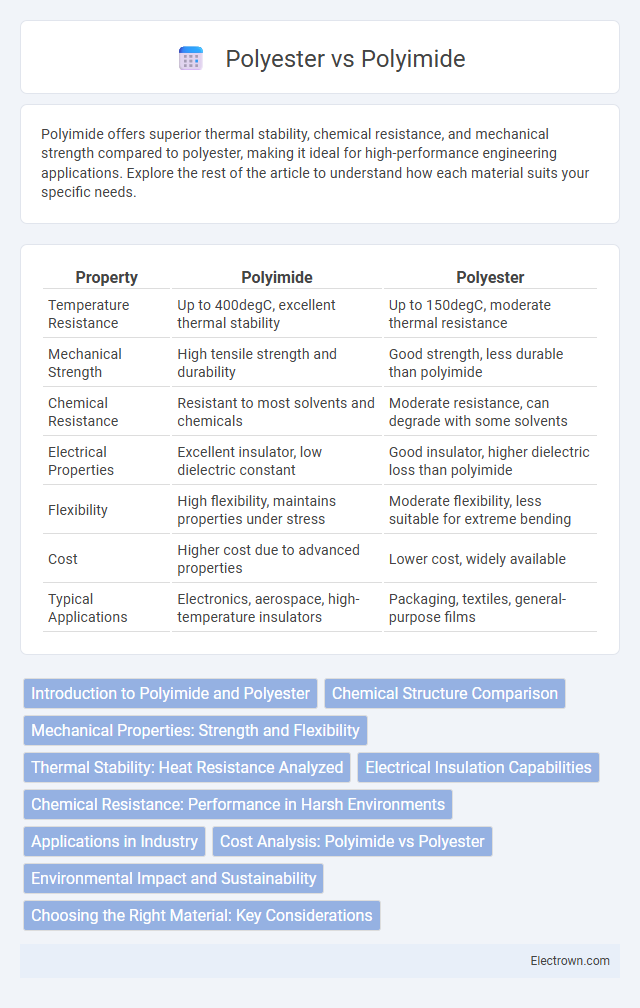
| Property | Polyimide | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC, excellent thermal stability | Up to 150degC, moderate thermal resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Good strength, less durable than polyimide |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most solvents and chemicals | Moderate resistance, can degrade with some solvents |
| Electrical Properties | Excellent insulator, low dielectric constant | Good insulator, higher dielectric loss than polyimide |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, maintains properties under stress | Moderate flexibility, less suitable for extreme bending |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Applications | Electronics, aerospace, high-temperature insulators | Packaging, textiles, general-purpose films |
Introduction to Polyimide and Polyester
Polyimide and polyester are two distinct polymers widely used in industrial and commercial applications due to their unique properties. Polyimide is renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance electronics, aerospace, and automotive components. Polyester offers excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to moisture, commonly utilized in textiles, packaging, and plastic bottles, making it a versatile choice for your everyday products.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyimide features a rigid aromatic backbone with imide groups, providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, while polyester consists of ester linkages connecting aromatic or aliphatic units, offering flexibility but lower heat tolerance. The imide rings in polyimide create strong intermolecular interactions, enhancing mechanical strength compared to the ester bonds in polyester, which are more susceptible to hydrolysis. Your choice between these polymers depends on the need for high-performance materials that withstand extreme conditions (polyimide) versus cost-effective, versatile options suitable for everyday applications (polyester).
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polyimide exhibits superior mechanical strength and exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining stability and toughness under extreme conditions compared to polyester. Polyester offers good flexibility and moderate tensile strength but tends to degrade at higher temperatures and under prolonged mechanical stress. The molecular structure of polyimide provides enhanced durability and resistance to deformation, making it ideal for high-performance engineering applications where both strength and flexibility are critical.
Thermal Stability: Heat Resistance Analyzed
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyester, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 400degC, while polyester typically degrades around 150-250degC. The imide rings in polyimide's molecular structure provide exceptional heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications such as aerospace and electronics. In contrast, polyester's ester linkages are more susceptible to thermal hydrolysis, limiting its use to lower temperature environments.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polyimide exhibits superior electrical insulation capabilities compared to polyester, withstanding higher temperatures up to 400degC without significant degradation in dielectric properties. The polymer's inherent thermal stability and excellent dielectric strength enable its use in demanding electronic applications such as flexible printed circuit boards and insulating films. In contrast, polyester typically offers good insulation up to around 150degC but suffers reduced performance at elevated temperatures, limiting its use in high-temperature electrical environments.
Chemical Resistance: Performance in Harsh Environments
Polyimide exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyester, maintaining structural integrity when exposed to harsh solvents, acids, and bases commonly encountered in industrial applications. Your choice of polyimide ensures reliable performance in extreme environments due to its high thermal stability and resistance to oxidative degradation. Polyester, while cost-effective, typically degrades faster under aggressive chemical exposure, making polyimide the preferred material for demanding chemical resistance.
Applications in Industry
Polyimide is extensively used in aerospace, electronics, and automotive industries due to its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties. Polyester finds widespread applications in packaging, textiles, and plastic bottles, benefiting from its durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Industrial sectors prioritize polyimide for high-performance insulation and flexible printed circuits, while polyester is favored for mass-produced consumer goods and structural components.
Cost Analysis: Polyimide vs Polyester
Polyimide typically incurs higher costs than polyester due to its advanced thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace and electronics. Polyester offers a more budget-friendly option with decent strength and flexibility, favored in textiles and packaging industries. Your choice should balance performance needs against budget constraints, as polyimide delivers superior durability while polyester provides cost-effective versatility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it more durable and potentially reducing waste through longer product lifecycles compared to polyester. However, polyester is generally derived from petroleum but has seen advancements in bio-based variants and recyclability, contributing to lower environmental footprints. The environmental impact of polyimide is higher due to energy-intensive manufacturing and limited recyclability, while polyester benefits from established recycling infrastructures and ongoing improvements in biodegradable formulations.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance applications like electronics and aerospace. Polyester provides cost-effective versatility with good dimensional stability and moderate heat resistance, suitable for everyday textiles and packaging. Evaluating factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, mechanical requirements, and budget constraints is critical when choosing between polyimide and polyester.
polyimide vs polyester Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com