Servo motors provide precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration through feedback systems, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Stepper motors move in discrete steps without feedback, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness for applications requiring precise open-loop control; explore the detailed comparison to determine which motor suits Your needs best.
Table of Comparison
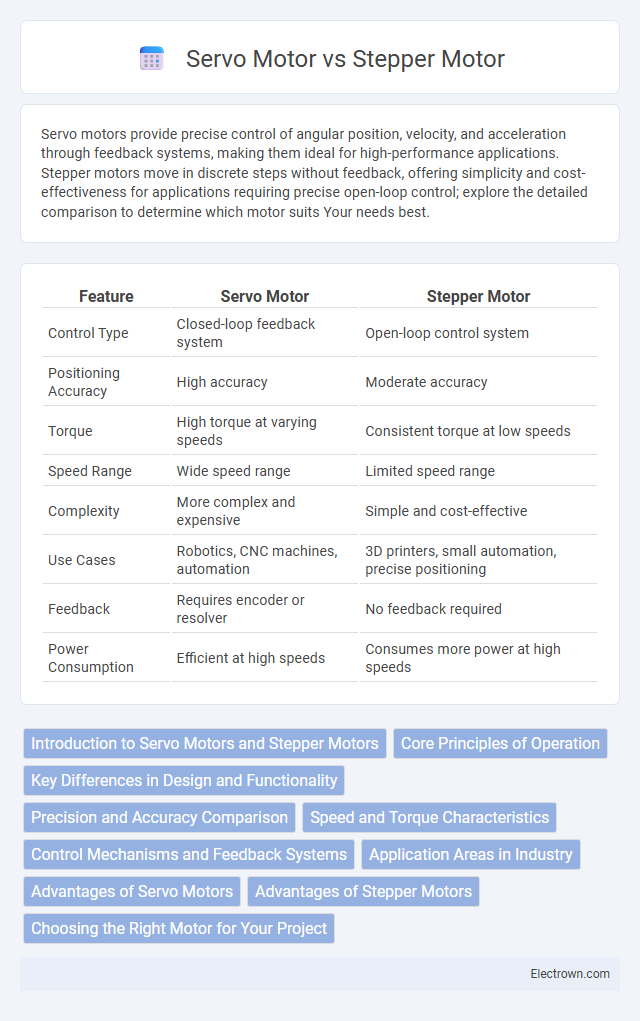
| Feature | Servo Motor | Stepper Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Closed-loop feedback system | Open-loop control system |
| Positioning Accuracy | High accuracy | Moderate accuracy |
| Torque | High torque at varying speeds | Consistent torque at low speeds |
| Speed Range | Wide speed range | Limited speed range |
| Complexity | More complex and expensive | Simple and cost-effective |
| Use Cases | Robotics, CNC machines, automation | 3D printers, small automation, precise positioning |
| Feedback | Requires encoder or resolver | No feedback required |
| Power Consumption | Efficient at high speeds | Consumes more power at high speeds |
Introduction to Servo Motors and Stepper Motors
Servo motors offer precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration using feedback systems like encoders, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and dynamic response. Stepper motors move in discrete steps without feedback, providing open-loop control with simpler design and reliable repeatability, commonly used in 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotics. Understanding the fundamental differences in operation, control mechanisms, and performance characteristics is crucial for selecting the appropriate motor type in automation and motion control systems.
Core Principles of Operation
Servo motors operate using a closed-loop control system that continuously monitors position, speed, and torque through feedback sensors, allowing precise control of motion and high accuracy in dynamic applications. Stepper motors function through open-loop control by moving in fixed angular increments or steps, controlled by electrical pulses, which makes them ideal for precise position control without feedback but limits their speed and torque capabilities. The core principle distinguishing servo motors is their ability to adjust output based on real-time feedback, whereas stepper motors rely on predetermined step sequences for positioning.
Key Differences in Design and Functionality
Servo motors use a closed-loop system with feedback to precisely control angular position, speed, and torque, while stepper motors operate in an open-loop system by moving in fixed steps without feedback. Servo motors provide higher efficiency, faster response, and smoother motion due to continuous rotation capability, whereas stepper motors excel in simpler control and holding torque at low speeds. Your choice depends on application requirements for precision, speed, and complexity in control systems.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Servo motors provide higher precision and accuracy due to their closed-loop feedback systems, which continuously monitor and adjust position in real-time, achieving resolutions of up to 0.001 degrees. Stepper motors operate in open-loop mode and move in fixed increments, often resulting in less precise control, with typical step angles ranging from 1.8 to 0.9 degrees. For applications requiring fine positioning, servo motors outperform stepper motors by offering smoother motion and reduced positional error.
Speed and Torque Characteristics
Servo motors offer high torque at variable speeds, maintaining consistent performance across a wide speed range, making them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control and dynamic torque output. Stepper motors provide high torque at low speeds but their torque decreases significantly at higher speeds, which can lead to missed steps and reduced accuracy. Understanding these speed and torque characteristics helps you select the right motor for your application's performance and precision requirements.
Control Mechanisms and Feedback Systems
Servo motors utilize closed-loop control systems with continuous feedback from encoders or resolvers to precisely adjust position, speed, and torque, ensuring high accuracy and dynamic response. Stepper motors operate primarily in open-loop control, moving in fixed increments without feedback, although some advanced systems incorporate sensors for improved precision. Choosing your motor depends on whether you require the precision and adaptability of servo feedback or the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of stepper control.
Application Areas in Industry
Servo motors are widely used in robotics, CNC machinery, and conveyor systems where precise control of speed, position, and torque is essential. Stepper motors excel in applications such as 3D printers, automated assembly equipment, and textile machines that require accurate low-speed positioning without feedback systems. Both motor types are integral to industrial automation, with servo motors favored for high-performance tasks and stepper motors preferred for cost-effective, simple positioning solutions.
Advantages of Servo Motors
Servo motors offer precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and dynamic response. They provide higher torque at high speeds compared to stepper motors, improving overall system efficiency in robotics and CNC machinery. Your project benefits from smoother motion and better load handling due to the closed-loop feedback system inherent to servo motors.
Advantages of Stepper Motors
Stepper motors offer precise position control without needing feedback systems, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate, repeatable movements. Their simple design results in high reliability and low maintenance costs compared to servo motors. Additionally, stepper motors provide excellent torque at low speeds, enhancing performance in CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics.
Choosing the Right Motor for Your Project
Selecting between a servo motor and a stepper motor depends on precision, speed, and torque requirements. Servo motors offer high torque, smooth operation, and closed-loop feedback ideal for applications demanding accuracy and dynamic response. Stepper motors provide simpler control and cost-effectiveness for projects with moderate speed and precision needs where open-loop control suffices.
Servo Motor vs Stepper Motor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com